Google Scholar Cite API
Our Google Scholar Cite API allows you to scrape cite results from the Google Scholar organic results.
The API endpoint is https://serpapi.com/search?engine=google_scholar_cite
Head to the playground for a live and interactive demo.
API Parameters
Search Query
q
Required
Parameter defines the ID of an individual Google Scholar organic search result. You can find the ID inside the result_id by using our Google Scholar API.
Localization
hl
Optional
Parameter defines the language to use for the Google Scholar Cite. It's a two-letter language code. (e.g., en for English, es for Spanish, or fr for French). Head to the Google languages page for a full list of supported Google languages.
 Serpapi Parameters
Serpapi Parameters
no_cache
Optional
Parameter will force SerpApi to fetch the Google Scholar Cite results even if a cached version is already present. A cache is served only if the query and all parameters are exactly the same. Cache expires after 1h. Cached searches are free, and are not counted towards your searches per month. It can be set to false (default) to allow results from the cache, or true to disallow results from the cache. no_cache and async parameters should not be used together.
async
Optional
Parameter defines the way you want to submit your search to SerpApi. It can be set to false (default) to open an HTTP connection and keep it open until you got your search results, or true to just submit your search to SerpApi and retrieve them later. In this case, you'll need to use our Searches Archive API to retrieve your results. async and no_cache parameters should not be used together. async should not be used on accounts with Ludicrous Speed enabled.
zero_trace
Optional
Enterprise only. Parameter enables ZeroTrace mode. It can be set to false (default) or true. Enable this mode to skip storing search parameters, search files, and search metadata on our servers. This may make debugging more difficult.
output
Optional
Parameter defines the final output you want. It can be set to json (default) to get a structured JSON of the results, or html to get the raw html retrieved.
json_restrictor
Optional
Parameter defines the fields you want to restrict in the outputs for smaller, faster responses. See JSON Restrictor for more details.
API Results
JSON Results
JSON output includes structured data for scholar cite results.
A search status is accessible through search_metadata.status. It flows this way: Processing -> Success || Error. If a search has failed, error will contain an error message. search_metadata.id is the search ID inside SerpApi.
HTML Results
HTML output is useful to debug JSON results or support features not supported yet by SerpApi.
HTML output gives you the raw HTML results from Google.
JSON structure overview
{
...
"citations": [
{
"title": "String - Citation title",
"snippet": "String - Citation snippet"
},
],
"links": [
{
"name": "String - Link name. E.g BibTeX, EndNote, RefMan, RefWorks",
"link": "String - Link URL"
},
]
...
}
API Examples
Example with q: FDc6HiktlqEJ
To acquire the ID for this search, first make a GET request to our Google Scholar API and either grab the result_id or the serpapi_cite_link, which are both located inside the Organic Results. Second, make a GET request to our Google Scholar Cite API with the acquired ID or link.
When SerpApi encounters cite results, we add them to our JSON output as the citations and links array. For each citations result, we are able to extract its title and snippet, and for each links result, we are able to extract its name and link.Links are expired shortly after the search is completed.
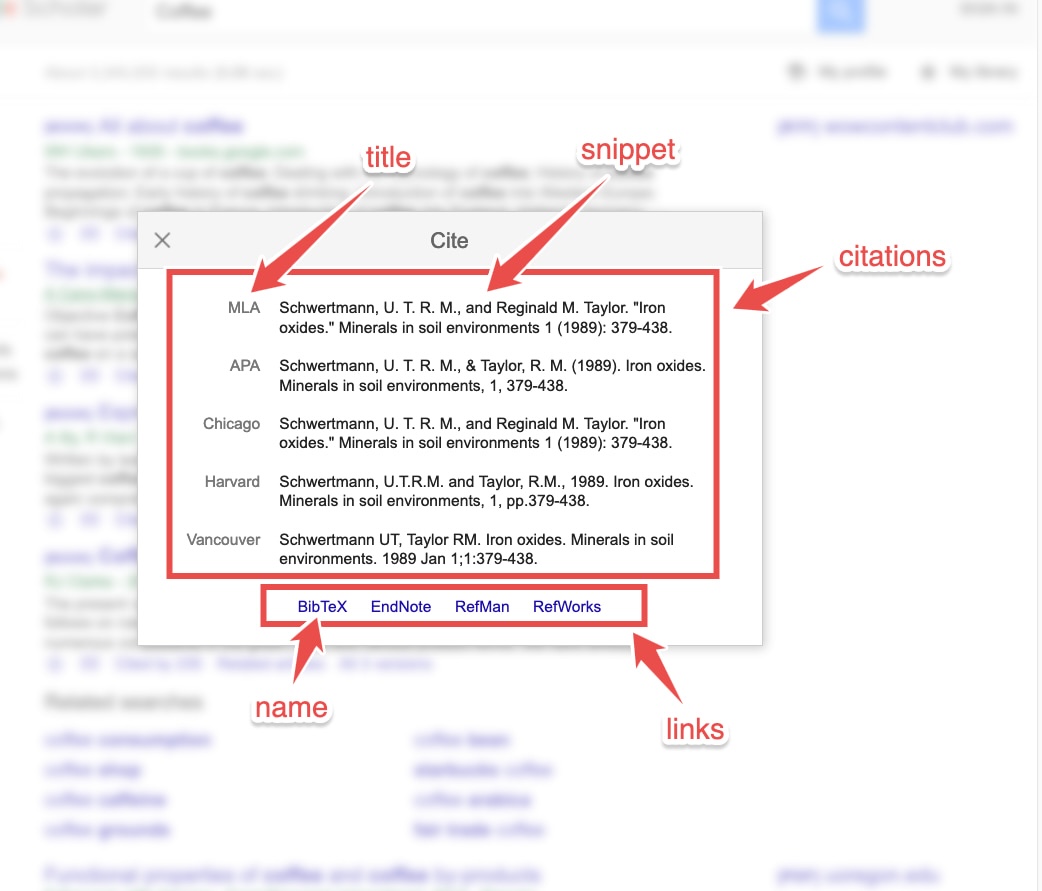
{
"search_metadata": {
"id": "66617537ab6e333342bd547b",
"status": "Success",
"json_endpoint": "https://serpapi.com/searches/aaa8f881f6ec4224/66617537ab6e333342bd547b.json",
"created_at": "2024-06-06 08:37:11 UTC",
"processed_at": "2024-06-06 08:37:11 UTC",
"google_scholar_cite_url": "https://scholar.google.com/scholar?q=info:FDc6HiktlqEJ:scholar.google.com&output=cite",
"raw_html_file": "https://serpapi.com/searches/aaa8f881f6ec4224/66617537ab6e333342bd547b.html",
"prettify_html_file": "https://serpapi.com/searches/aaa8f881f6ec4224/66617537ab6e333342bd547b.prettify",
"total_time_taken": 1.57
},
"search_parameters": {
"engine": "google_scholar_cite",
"q": "FDc6HiktlqEJ"
},
"citations": [
{
"title": "MLA",
"snippet": "Schwertmann, U. T. R. M., and Reginald M. Taylor. Iron oxides. Minerals in soil environments 1 (1989): 379-438."
},
{
"title": "APA",
"snippet": "Schwertmann, U. T. R. M., & Taylor, R. M. (1989). Iron oxides. Minerals in soil environments, 1, 379-438."
},
{
"title": "Chicago",
"snippet": "Schwertmann, U. T. R. M., and Reginald M. Taylor. Iron oxides. Minerals in soil environments 1 (1989): 379-438."
},
{
"title": "Harvard",
"snippet": "Schwertmann, U.T.R.M. and Taylor, R.M., 1989. Iron oxides. Minerals in soil environments, 1, pp.379-438."
},
{
"title": "Vancouver",
"snippet": "Schwertmann UT, Taylor RM. Iron oxides. Minerals in soil environments. 1989 Jan 1;1:379-438."
}
],
"links": [
{
"name": "BibTeX",
"link": "https://scholar.googleusercontent.com/scholar.bib?q=info:FDc6HiktlqEJ:scholar.google.com/&output=citation&scisdr=ClGWBVL5GAA:AFWwaeYAAAAAZmF3lHkz3kdCUVvSbM5C_Msq62Q&scisig=AFWwaeYAAAAAZmF3lBXgwnMk3BS3W9KIJ9XaCUs&scisf=4&ct=citation&cd=-1&hl=en"
},
{
"name": "EndNote",
"link": "https://scholar.googleusercontent.com/scholar.enw?q=info:FDc6HiktlqEJ:scholar.google.com/&output=citation&scisdr=ClGWBVL5GAA:AFWwaeYAAAAAZmF3lHkz3kdCUVvSbM5C_Msq62Q&scisig=AFWwaeYAAAAAZmF3lBXgwnMk3BS3W9KIJ9XaCUs&scisf=3&ct=citation&cd=-1&hl=en"
},
{
"name": "RefMan",
"link": "https://scholar.googleusercontent.com/scholar.ris?q=info:FDc6HiktlqEJ:scholar.google.com/&output=citation&scisdr=ClGWBVL5GAA:AFWwaeYAAAAAZmF3lHkz3kdCUVvSbM5C_Msq62Q&scisig=AFWwaeYAAAAAZmF3lBXgwnMk3BS3W9KIJ9XaCUs&scisf=2&ct=citation&cd=-1&hl=en"
},
{
"name": "RefWorks",
"link": "https://scholar.googleusercontent.com/scholar.rfw?q=info:FDc6HiktlqEJ:scholar.google.com/&output=citation&scisdr=ClGWBVL5GAA:AFWwaeYAAAAAZmF3lHkz3kdCUVvSbM5C_Msq62Q&scisig=AFWwaeYAAAAAZmF3lBXgwnMk3BS3W9KIJ9XaCUs&scisf=1&ct=citation&cd=-1&hl=en"
}
]
}