Bing Copilot API
Our Bing Copilot API allows you to scrape results from the Bing Copilot page. The API is accessed through the following endpoint: /search?engine=bing_copilot.
A user may query the following: https://serpapi.com/search?engine=bing_copilot utilizing a GET request. Head to the playground for a live and interactive demo.
Note on Query Language Support
Bing Copilot API does not support explicit language parameter. However, the return language could be specified inside the query. Example query: Coffee, return results in Korean.
In most cases, Copilot complies with the requested language. However, given that it is an AI model, the final language is not guaranteed.
API Parameters
 Serpapi Parameters
Serpapi Parameters
no_cache
Optional
Parameter will force SerpApi to fetch the Bing Copilot results even if a cached version is already present. A cache is served only if the query and all parameters are exactly the same. Cache expires after 1h. Cached searches are free, and are not counted towards your searches per month. It can be set to false (default) to allow results from the cache, or true to disallow results from the cache. no_cache and async parameters should not be used together.
async
Optional
Parameter defines the way you want to submit your search to SerpApi. It can be set to false (default) to open an HTTP connection and keep it open until you got your search results, or true to just submit your search to SerpApi and retrieve them later. In this case, you'll need to use our Searches Archive API to retrieve your results. async and no_cache parameters should not be used together. async should not be used on accounts with Ludicrous Speed enabled.
zero_trace
Optional
Enterprise only. Parameter enables ZeroTrace mode. It can be set to false (default) or true. Enable this mode to skip storing search parameters, search files, and search metadata on our servers. This may make debugging more difficult.
output
Optional
Parameter defines the final output you want. It can be set to json (default) to get a structured JSON of the results, or html to get the raw html retrieved.
json_restrictor
Optional
Parameter defines the fields you want to restrict in the outputs for smaller, faster responses. See JSON Restrictor for more details.
API Results
JSON Results
JSON output includes structured data for text_blocks and references.
A search status is accessible through search_metadata.status. It flows this way: Processing -> Success || Error. If a search has failed, error will contain an error message. search_metadata.id is the search ID inside SerpApi.
HTML Results
HTML output is useful to debug JSON results or support features not supported yet by SerpApi. HTML output gives you the raw HTML results from Bing Copilot.
API Examples
Example for table in text_blocks
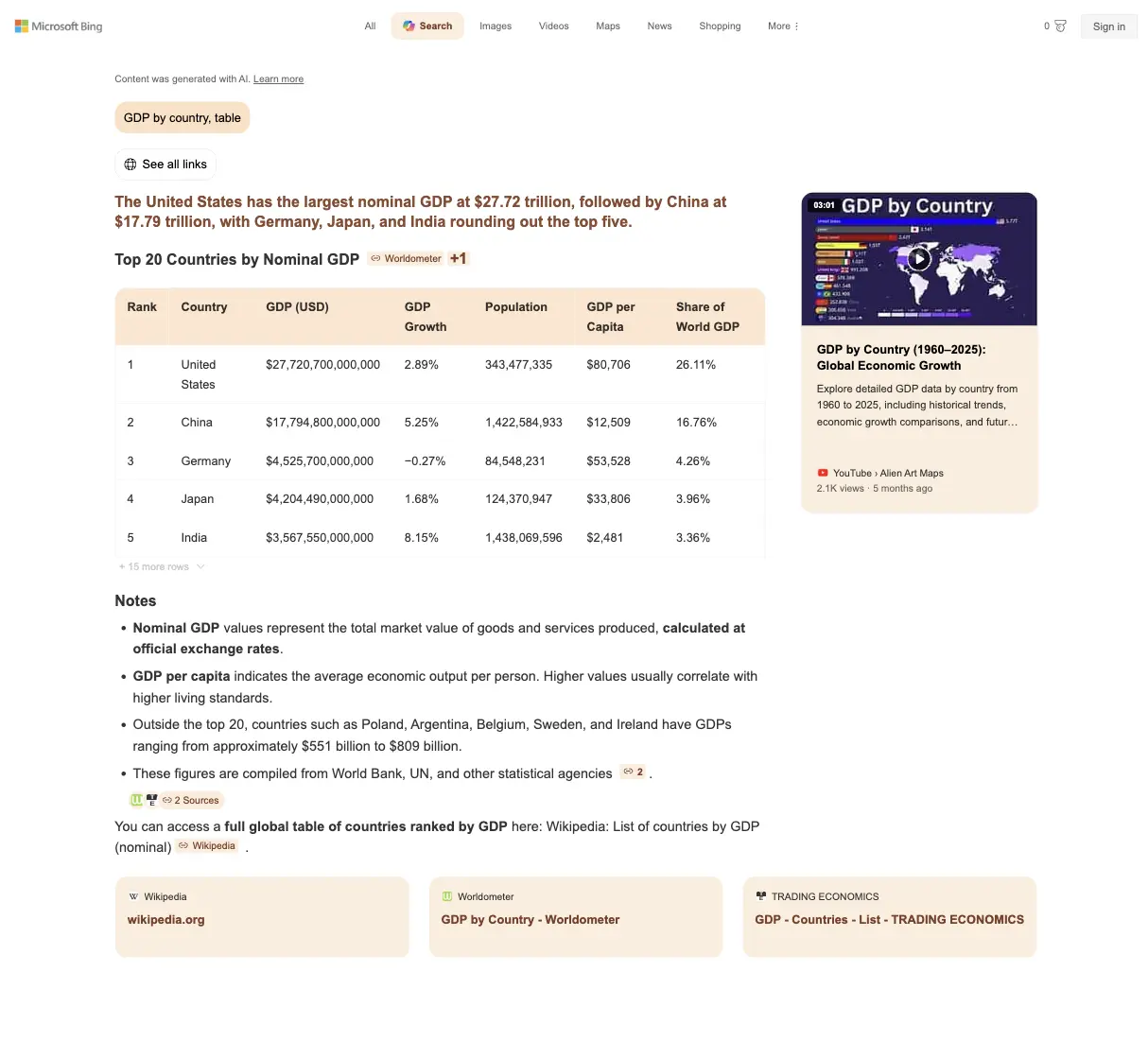
{
"search_metadata": {
"id": "...",
"status": "Success",
"bing_copilot_url": "https://www.bing.com/copilotsearch?q=GDP+by+country%2C+table&FORM=CSSCOP",
"json_endpoint": "...",
"raw_html_file": "...",
"total_time_taken": 12.55
},
"search_parameters": {
"engine": "bing_copilot",
"q": "GDP by country, table"
},
"header": "The United States has the largest nominal GDP at $27.72 trillion, followed by China at $17.79 trillion, with Germany, Japan, and India rounding out the top five.",
"header_video": {
"title": "GDP by Country (1960–2025): Global Economic Growth",
"link": "https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uUth2BKgAp8",
"duration": "03:01",
"thumbnail": "https://th.bing.com/th/id/OVP.qD_scwJNYuaGYeS5zYKMswEsDh?w=312&h=176&c=7&rs=1&qlt=90&o=6&pid=1.7",
"channel": "Alien Art Maps",
"views": "2.1K views",
"published": "5 months ago"
},
"text_blocks": [
{
"type": "heading",
"snippet": "Top 20 Countries by Nominal GDP Worldometer+1",
"level": 2,
"snippet_links": [
{ "text": "Top 20 Countries by Nominal GDP", "link": "https://www.worldometers.info/gdp/gdp-by-country/" }
],
"reference_indexes": [1, 2]
},
{
"type": "table",
"headers": [
"Rank", "Country", "GDP (USD)", "GDP Growth", "Population", "GDP per Capita", "Share of World GDP"
],
"table": [
["1", "United States", "$27,720,700,000,000", "2.89%", "343,477,335", "$80,706", "26.11%"],
["2", "China", "$17,794,800,000,000", "5.25%", "1,422,584,933", "$12,509", "16.76%"],
...
],
"formatted": [
{"rank": "1", "country": "United States", "gdp_usd": "$27,720,700,000,000", "gdp_growth": "2.89%", "population": "343,477,335", "gdp_per_capita": "$80,706", "share_of_world_gdp": "26.11%"},
{"rank": "2", "country": "China", "gdp_usd": "$17,794,800,000,000", "gdp_growth": "5.25%", "population": "1,422,584,933", "gdp_per_capita": "$12,509", "share_of_world_gdp": "16.76%"},
...
]
},
{
"type": "list",
"list": [
{
"snippet": "Nominal GDP values represent the total market value of goods and services produced, calculated at official exchange rates.",
"snippet_highlighted_words": ["Nominal GDP", "calculated at official exchange rates"]
},
{
"snippet": "GDP per capita indicates the average economic output per person. Higher values usually correlate with higher living standards.",
"snippet_highlighted_words": ["GDP per capita"]
},
{
"snippet": "These figures are compiled from World Bank, UN, and other statistical agencies 2.",
"snippet_links": [
{ "text": "These figures are compiled from World Bank, UN, and other statistical agencies", "link": "https://www.worldometers.info/gdp/gdp-by-country/" }
],
"reference_indexes": [1, 2]
}
]
},
{
"type": "paragraph",
"snippet": "You can access a full global table of countries ranked by GDP here: Wikipedia: List of countries by GDP (nominal)Wikipedia .",
"snippet_links": [
{ "text": "You can access a full global table of countries ranked by GDP here: Wikipedia: List of countries by GDP (nominal)", "link": "https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_countries_by_GDP_%28nominal%29" }
],
"snippet_highlighted_words": ["full global table of countries ranked by GDP"],
"reference_indexes": [0]
}
],
"references": [
{ "index": 0, "title": "wikipedia.org", "link": "https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_countries_by_GDP_%28nominal%29", "source": "Wikipedia" },
{ "index": 1, "title": "GDP by Country - Worldometer", "link": "https://www.worldometers.info/gdp/gdp-by-country/", "snippet": "Countries in the world ranked by Gross Domestic Product (GDP). ...", "source": "Worldometer" },
{ "index": 2, "title": "GDP - Countries - List - TRADING ECONOMICS", "link": "https://tradingeconomics.com/country-list/gdp", "snippet": "This page provides values for GDP reported in several countries. ...", "source": "TRADING ECONOMICS" }
]
}
Example for code_block in text_blocks
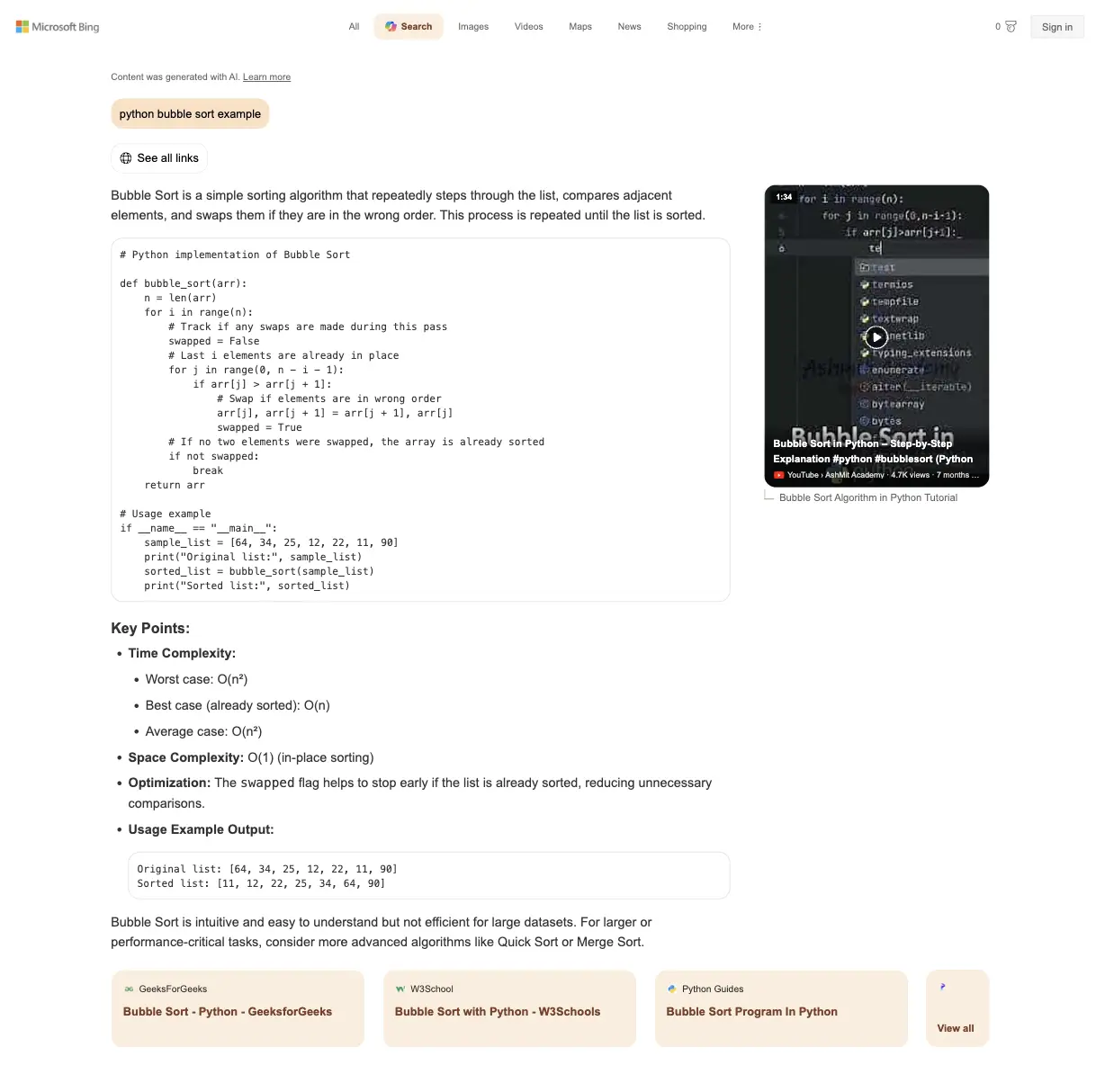
{
"search_metadata": {
"id": "...",
"status": "Success",
"bing_copilot_url": "https://www.bing.com/copilotsearch?q=python+bubble+sort+example&FORM=CSSCOP",
"json_endpoint": "...",
"raw_html_file": "...",
"total_time_taken": 8.64
},
"search_parameters": {
"engine": "bing_copilot",
"q": "python bubble sort example"
},
"header_video": {
"title": "Bubble Sort in Python – Step-by-Step Explanation #python #bubblesort (Python for beginners)",
"link": "https://www.bing.com/...",
"duration": "1:34",
"thumbnail": "https://th.bing.com/th/id/OVP.944uoCW0Lo4Wa8XhDbAJUgDKFo?w=312&h=424&c=7&rs=1&qlt=90&o=6&pid=1.7",
"channel": "AshMit Academy",
"views": "4.7K views",
"published": "7 months ago"
},
"text_blocks": [
{
"type": "paragraph",
"snippet": "Bubble Sort is a simple sorting algorithm that repeatedly steps through the list, compares adjacent elements, and swaps them if they are in the wrong order. This process is repeated until the list is sorted."
},
{
"type": "code_block",
"language": "python",
"code": "# Python implementation of Bubble Sort
def bubble_sort(arr):
n = len(arr)
for i in range(n):
# Track if any swaps are made during this pass
swapped = False
# Last i elements are already in place
for j in range(0, n - i - 1):
if arr[j] > arr[j + 1]:
# Swap if elements are in wrong order
arr[j], arr[j + 1] = arr[j + 1], arr[j]
swapped = True
# If no two elements were swapped, the array is already sorted
if not swapped:
break
return arr
# Usage example
if __name__ == "__main__":
sample_list = [64, 34, 25, 12, 22, 11, 90]
print("Original list:", sample_list)
sorted_list = bubble_sort(sample_list)
print("Sorted list:", sorted_list)"
},
{ "type": "heading", "snippet": "Key Points:", "level": 3 },
{
"type": "list",
"list": [
{ "snippet": "Time Complexity:", "snippet_highlighted_words": ["Time Complexity:"] },
{ "snippet": "Space Complexity: O(1) (in-place sorting)", "snippet_highlighted_words": ["Space Complexity:"] },
{ "snippet": "Optimization: The swapped flag helps to stop early if the list is already sorted, reducing unnecessary comparisons.", "snippet_highlighted_words": ["Optimization:"] },
{ "snippet": "Usage Example Output:", "snippet_highlighted_words": ["Usage Example Output:"] }
]
},
{ "type": "paragraph", "snippet": "Bubble Sort is intuitive and easy to understand but not efficient for large datasets. For larger or performance-critical tasks, consider more advanced algorithms like Quick Sort or Merge Sort." }
],
"references": [
{ "index": 0, "title": "Bubble Sort - Python - GeeksforGeeks", "link": "https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/python/python-program-for-bubble-sort/", "snippet": "The algorithm iterates through the array multiple times, with each pass pushing the largest unsorted element to its correct position at the end. Code includes an optimization: if n…", "source": "GeeksForGeeks" },
{ "index": 1, "title": "Bubble Sort with Python - W3Schools", "link": "https://www.w3schools.com/python/python_dsa_bubblesort.asp", "snippet": "Run the simulation to see how it looks like when the Bubble Sort algorithm sorts an array of values. Each value in the array is represented by a column. The word 'Bubble' comes fro…", "source": "W3School" },
{ "index": 2, "title": "Bubble Sort Program In Python", "link": "https://pythonguides.com/python-program-for-bubble-sort/", "snippet": "Learn how to implement Bubble Sort in Python with step-by-step practical examples. Simple explanations, multiple methods, and full code for beginners and pros.", "source": "Python Guides" }
]
}
Example for nested lists in text_blocks
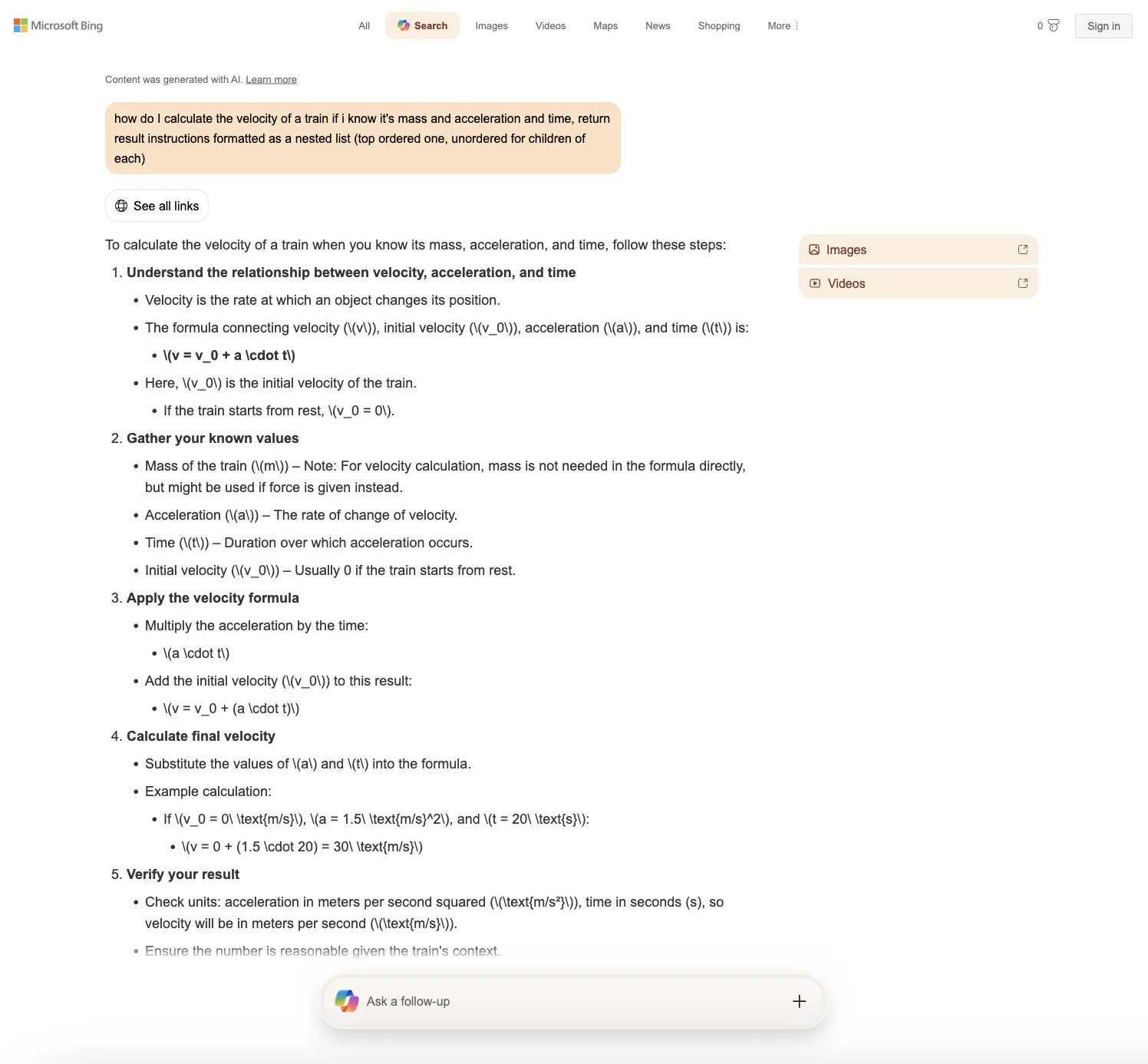
{
"search_metadata": {
"id": "...",
"status": "Success",
"bing_copilot_url": "https://www.bing.com/copilotsearch?q=how+do+I+calculate+the+velocity+of+a+train+...+nested+list&FORM=CSSCOP",
"json_endpoint": "...",
"raw_html_file": "...",
"total_time_taken": 8.02
},
"search_parameters": {
"engine": "bing_copilot",
"q": "how do I calculate the velocity of a train if i know it's mass and acceleration and time, return result instructions formatted as a nested list (top ordered one, unordered for children of each)"
},
"images_link": "https://www.bing.com/ck/a?!...",
"videos_link": "https://www.bing.com/ck/a?!...",
"text_blocks": [
{ "type": "paragraph", "snippet": "To calculate the velocity of a train when you know its mass, acceleration, and time, follow these steps:" },
{
"type": "list",
"list": [
{
"snippet": "Understand the relationship between velocity, acceleration, and time",
"snippet_highlighted_words": ["Understand the relationship between velocity, acceleration, and time"],
"list": [
{ "snippet": "Velocity is the rate at which an object changes its position." },
{
"snippet": "The formula connecting velocity (v), initial velocity (v_0), acceleration (a), and time (t) is:",
"list": [
{ "snippet": "\(v = v_0 + a \cdot t\)", "snippet_highlighted_words": ["\(v = v_0 + a \cdot t\)"] }
]
},
{
"snippet": "Here, v_0 is the initial velocity of the train.",
"list": [ { "snippet": "If the train starts from rest, v_0 = 0." } ]
}
]
},
{
"snippet": "Apply the velocity formula",
"snippet_highlighted_words": ["Apply the velocity formula"],
"list": [
{ "snippet": "Multiply the acceleration by the time:", "list": [ { "snippet": "a \cdot t" } ] },
{ "snippet": "Add the initial velocity (v_0) to this result:", "list": [ { "snippet": "v = v_0 + (a \cdot t)" } ] }
]
},
{
"snippet": "Calculate final velocity",
"list": [
{ "snippet": "Substitute the values of a and t into the formula." },
{ "snippet": "Example calculation:", "list": [ { "snippet": "If v_0 = 0, a = 1.5 m/s^2, and t = 20 s:", "list": [ { "snippet": "v = 30 m/s" } ] } ] }
]
}
]
}
],
"references": [
{ "index": 0, "title": "Speed of Train | How to Calculate the Motion or Speed of a Train?", "link": "https://www.bing.com/ck/a?!...", "source": "www.learncbse.in" },
{ "index": 1, "title": "Velocity Calculator v = u + at", "link": "https://www.bing.com/ck/a?!...", "source": "Calculator Soup" },
{ "index": 2, "title": "Kinematic Equations - The Physics Classroom", "link": "https://www.bing.com/ck/a?!...", "source": "The Physics Classroom" },
{ "index": 3, "title": "Calculating Train Velocity ...", "link": "https://www.bing.com/ck/a?!...", "source": "YouTube" }
]
}
Example for header_video

{
"search_metadata": {
"id": "...",
"status": "Success",
"bing_copilot_url": "https://www.bing.com/copilotsearch?q=how+to+tie+a+tie&FORM=CSSCOP",
"json_endpoint": "...",
"raw_html_file": "...",
"total_time_taken": 10.94
},
"search_parameters": {
"engine": "bing_copilot",
"q": "how to tie a tie"
},
"header": "Tying a tie involves following simple steps to create a neat, symmetrical knot that complements your outfit, with the Windsor, Half Windsor, and Four-in-Hand being the most common knots.",
"header_video": {
"title": "How to tie a tie EASY WAY (Slowly & Mirrored) Windsor knot",
"link": "https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4fHMbXWcoq0",
"duration": "03:33",
"thumbnail": "https://th.bing.com/th/id/OVP.QoEtXG9S8m2p9pIBbBJAMAHgFo?w=312&h=200&c=7&rs=1&qlt=90&o=6&pid=1.7",
"source": "YouTube",
"channel": "How to tie a tie",
"views": "47.9M views",
"published": "Sep 3, 2020"
},
"text_blocks": [
{ "type": "heading", "snippet": "Choosing the Knot", "level": 2 },
{
"type": "list",
"list": [
{ "snippet": "Four-in-Hand Knot: Simple, slightly asymmetrical, works for most occasions and collar types.", "snippet_highlighted_words": ["Four-in-Hand Knot"] },
{ "snippet": "Half Windsor Knot: Medium size, symmetrical, suitable for work or formal events.", "snippet_highlighted_words": ["Half Windsor Knot"] },
...
]
},
{ "type": "heading", "snippet": "Step-by-Step: Four-in-Hand Knot (Beginner-Friendly)", "level": 2 },
{ "type": "list", "list": [ { "snippet": "Start Position: Drape the tie around your neck with the wide end on your right extending about 12 inches below the narrow end.", "snippet_highlighted_words": ["Start Position", "wide end on your right"] }, ... ] }
]
}
JSON structure overview
{
...
"header": "String - main answer heading",
"header_video": {
"title": "String - Title of the video",
"link": "String - URL to the video",
"duration": "String - Duration of the video",
"thumbnail": "String - URL to the video thumbnail",
"source": "String - Source of the video (e.g., YouTube)",
"channel": "String - Channel name",
"views": "String - Number of views",
"published": "String - Published date"
},
"images_link": "String (URL) - link to Bing Images for the query",
"videos_link": "String (URL) - link to Bing Videos for the query",
"text_blocks": [
{
"type": "paragraph",
"snippet": "String",
"snippet_links": [
{
"text": "String",
"link": "String"
}
],
"snippet_highlighted_words": "Array - Array of highlighted words",
"reference_indexes": "Array - Array of reference indexes"
},
{
"type": "heading",
"level": "Integer (1..6)",
"snippet": "String",
"snippet_links": "Array",
"snippet_highlighted_words": "Array - Array of highlighted words",
"reference_indexes": "Array - Array of reference indexes"
},
{
"type": "list",
"list": [
{
"snippet": "String",
"snippet_links": "Array",
"snippet_highlighted_words": "Array - Array of highlighted words",
"reference_indexes": "Array - Array of reference indexes",
}
]
},
{
"type": "code_block",
"code": "String",
"language": "String - Optional language"
},
{
"type": "table",
"headers": "Array - Array of header strings",
"table": "Array - Array of table rows (each row is an array of strings)"
"formatted": "Array"
}
],
"references": [
{
"index": "Integer (zero-based)",
"title": "String - Optional title",
"link": "String - URL to the reference",
"snippet": "String - Optional snippet text",
"source": "String - Optional source"
}
],
...
}