Want to grab Amazon product details—prices, ASINs, reviews, and more—by scraping them into your project? You're in the right place!
In this tutorial, we'll help you learn how to scrape products from Amazon, starting from the very beginning. We’ll show you how to do it yourself or use our Amazon Search API for simplicity.
Feel free to skip to the "API" version, for scalable and easier solution.
DIY Version: Step-by-Step Amazon Web Scraper
Important Note: This method is ideal for those who want to scrape data in small quantities only. Scraping Amazon data is subject to limitations, as Amazon actively attempts to block scraping bots. Therefore, the methods presented here should be used responsibly and within the boundaries of Amazon's terms of service. For production, you can utilize our Amazon Search API, which we also share in this post.
Prerequisites
Before we dive in, make sure you have the following:
- Basic Python knowledge (variables, functions, loops).
- Python installed (version 3.7+ recommended).
- Postman (recommended)
- A few Python libraries:
requests,beautifulSoupandpandasfor saving data.
You can install the necessary libraries with:
pip install requests beautifulsoup4 pandasCheck out our Web Scraping in Python tutorial to learn the basics of web scraping.

Step 1: Understanding the Target Page
Let's go to "https://www.amazon.com" and press F12 Or right-click and click on "Inspect" to open DevTools. In the devTools, click on the "Network" tab.
After that, make a search in the search bar, for example, "coffee". You'll notice the network logs start changing and a file with the "document" type appears.
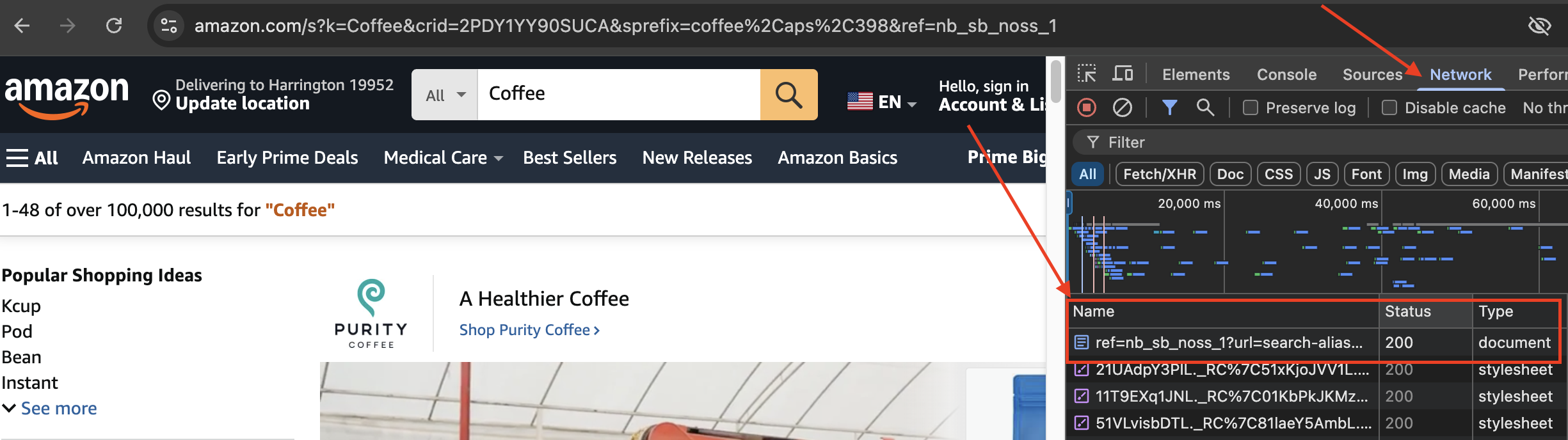
Click on that and examine the response tab.
Let's look for a-section a-spacing-base desktop-grid-content-view by using ctrl or cmd + f
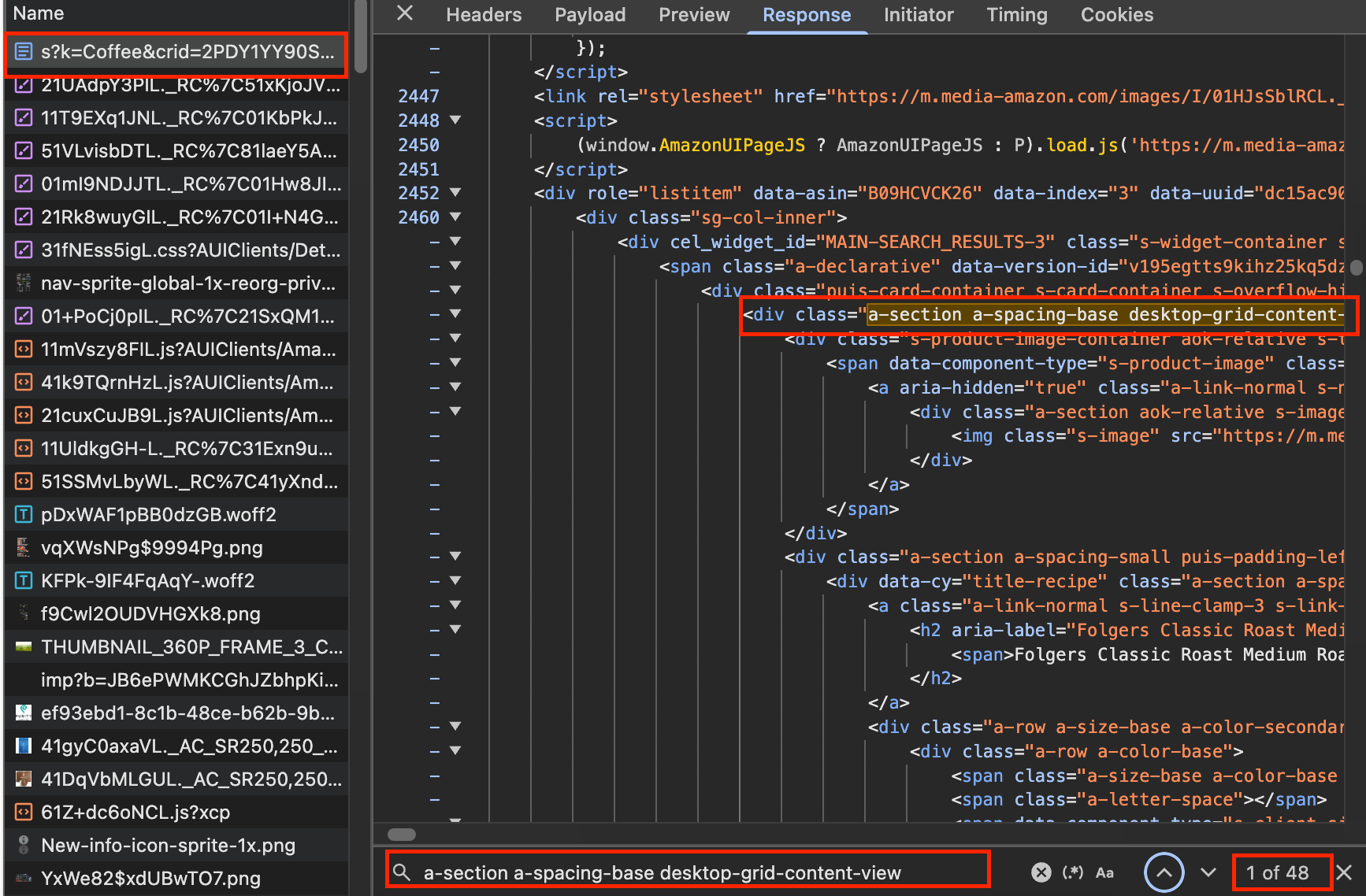
Why need to look for a-section a-spacing-base desktop-grid-content-view?
Let's go back to the "Elements" tab and click on this arrow icon
It allows us to hover over the products and identify the HTML tags used.
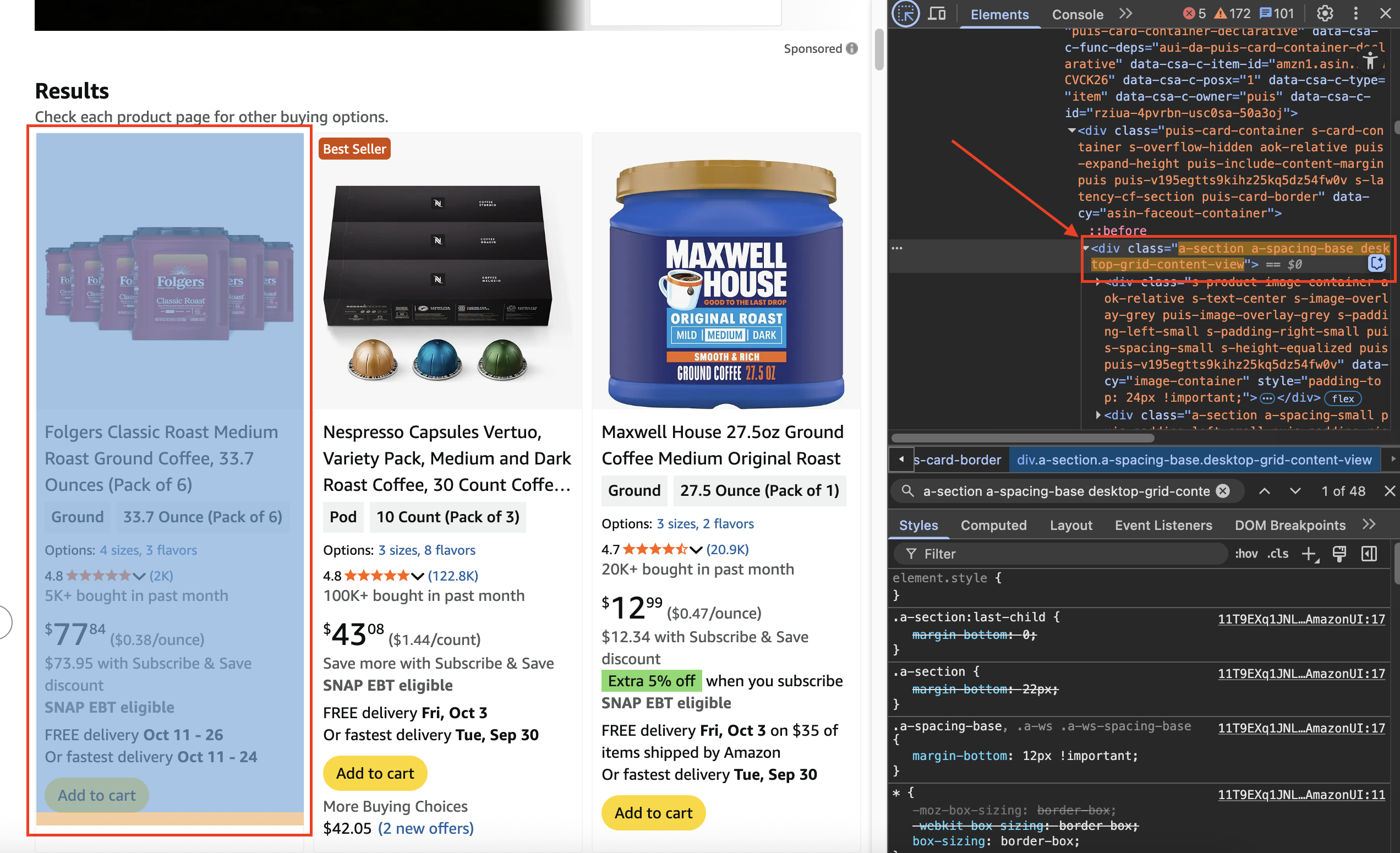
Now that we are able to identify that this endpoint will give us the same results as the homepage. Let's make the requests.
Step 2: Making the First Requests
Let's go back to the "Network" tabs and copy the log as cURL
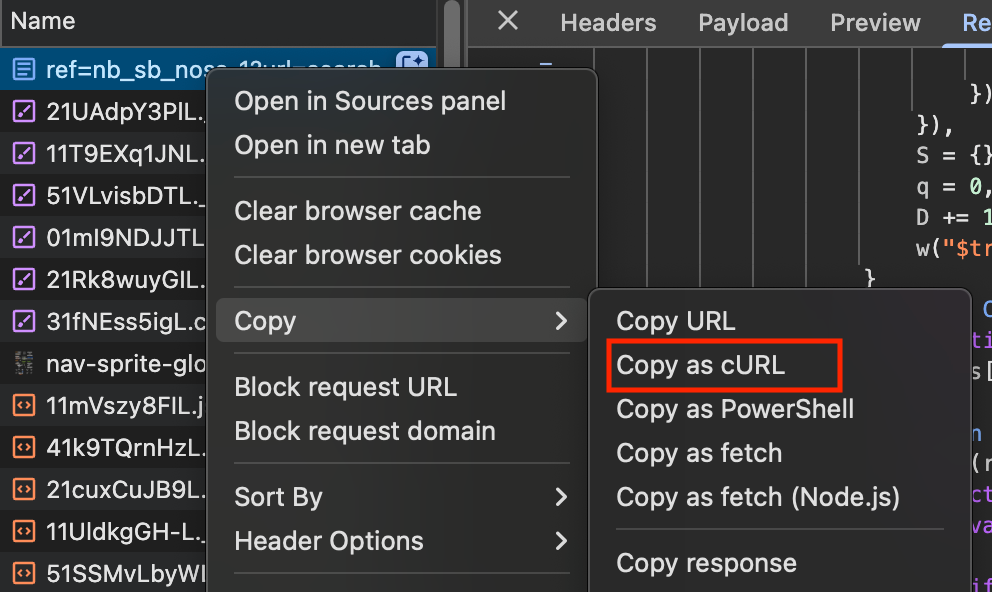
Open Postman and paste this value. We will get the same response as previously. You can take some time here to explore the "Params" and "Headers" on Postman.
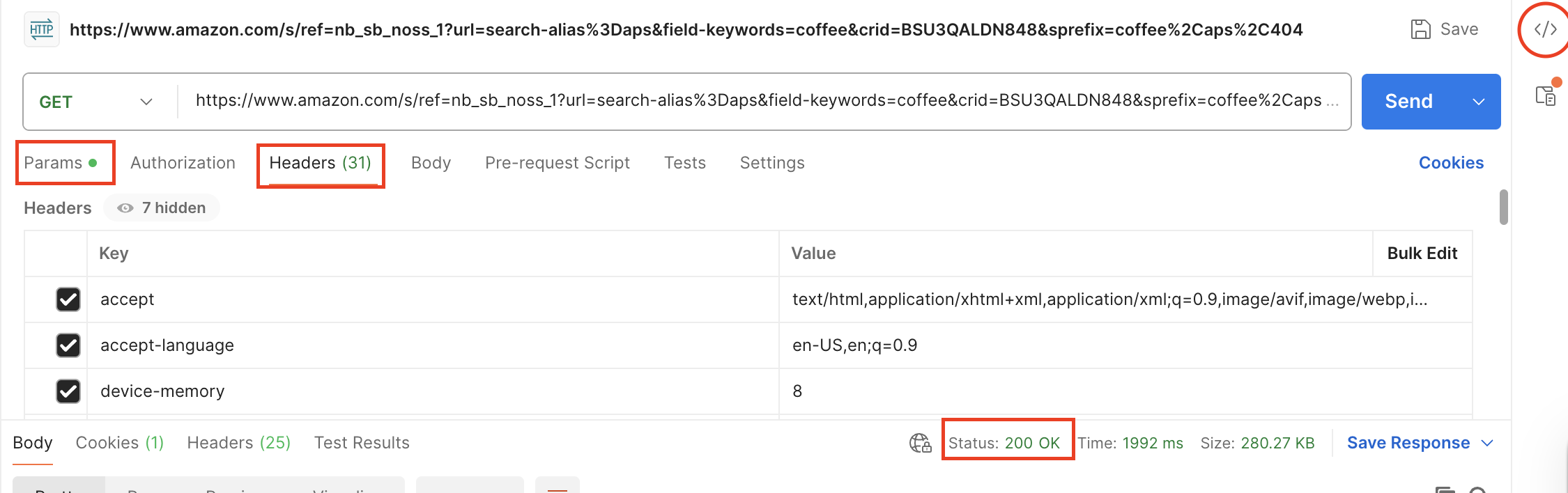
Now, let's click on the </> icon in Postman. This will generate a code sample for us on how to send requests in Python and other languages as well. It will generate something like this:
import requests
url = "https://www.amazon.com/s/ref=nb_sb_noss_1?url=search-alias%3Daps&field-keywords=coffee&crid=BSU3QALDN848&sprefix=coffee%2Caps%2C404"
payload = {}
headers = {
# This value is intentionally left blank. Make sure to fill it in with actual headers from Postman to mimic a real browser request.
}
response = requests.request("GET", url, headers=headers, data=payload)
print(response.text)Let's copy and paste the code into our code editor.
Step 3: Parsing the HTML
To parse the HTML, we'll use BeautifulSoup. First, we need to identify the relevant HTML tags or elements. Let's go back to the browser and hover over the product. Let's try to get the "Product Name", "Stars Rating", "Number of Ratings", and "Price"
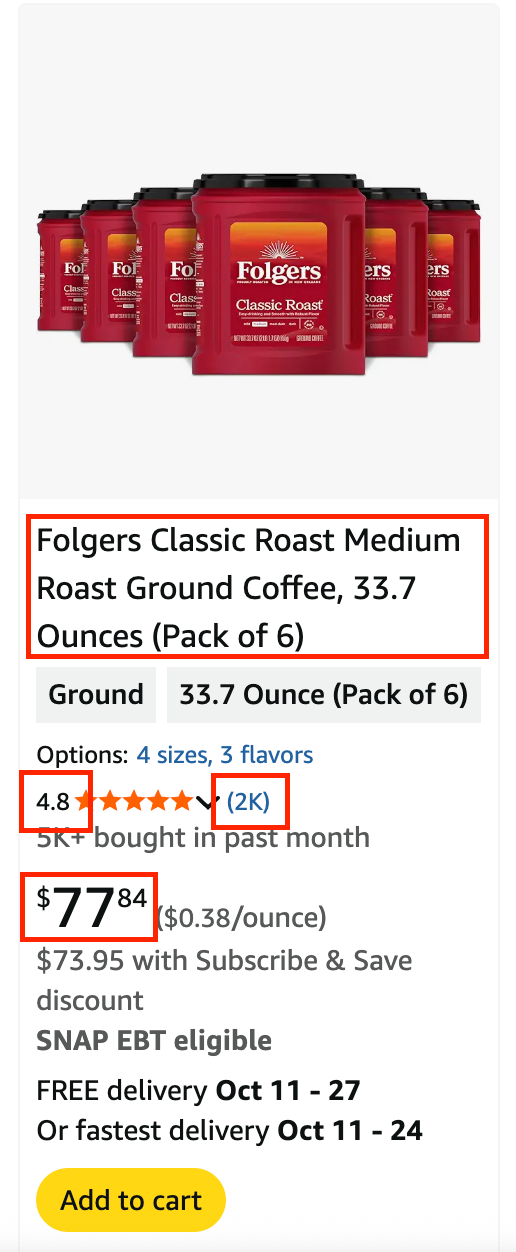
Firstly, we need to identify the element for product containers
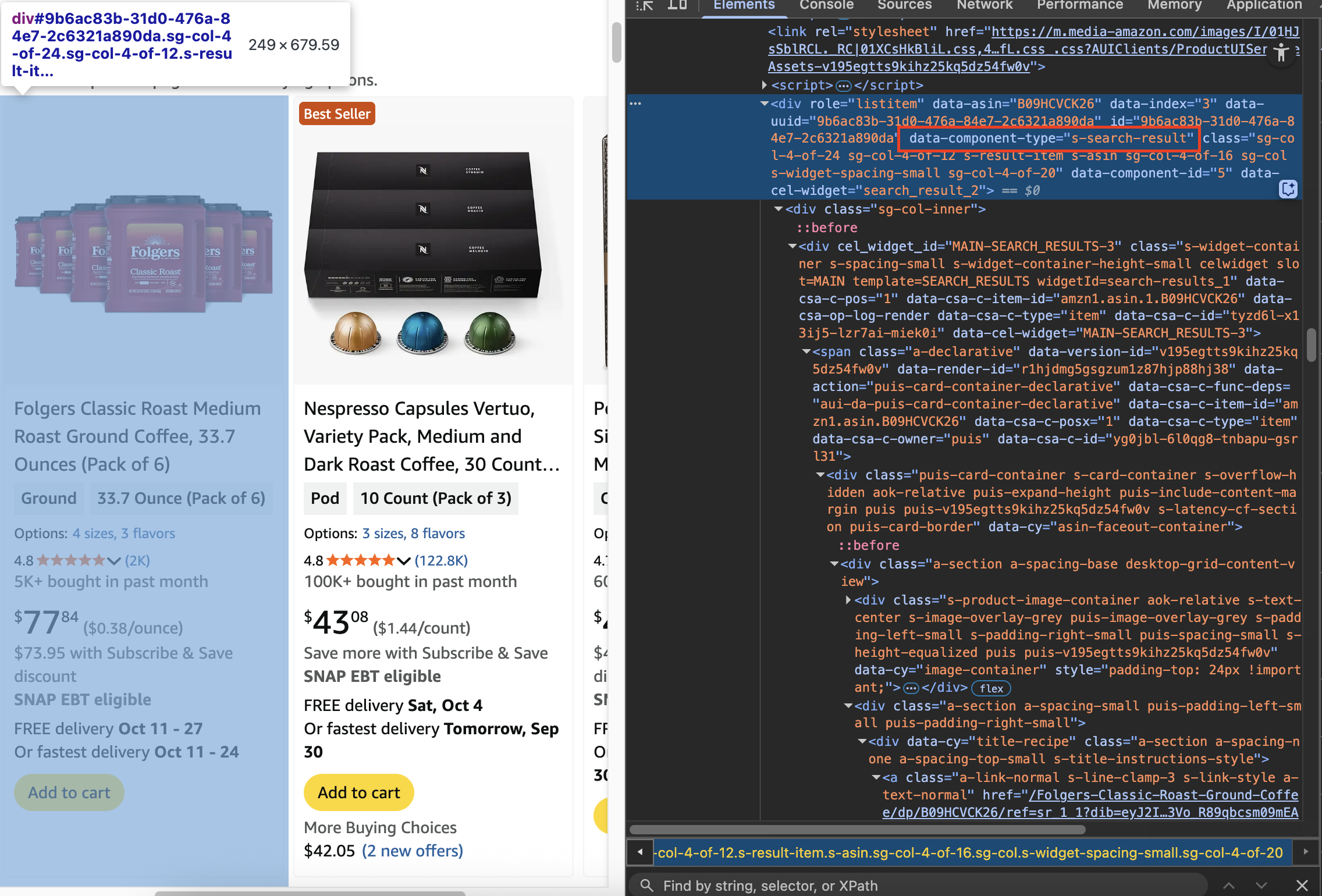
soup = BeautifulSoup(response.text, 'html.parser')
# Find all product containers
product_containers = soup.find_all('div', {'data-component-type': 's-search-result'})
print(f"Found {len(product_containers)} product containers")
Now, let's focus on the first product first
container = product_containers[0]Scrape "Product Name"
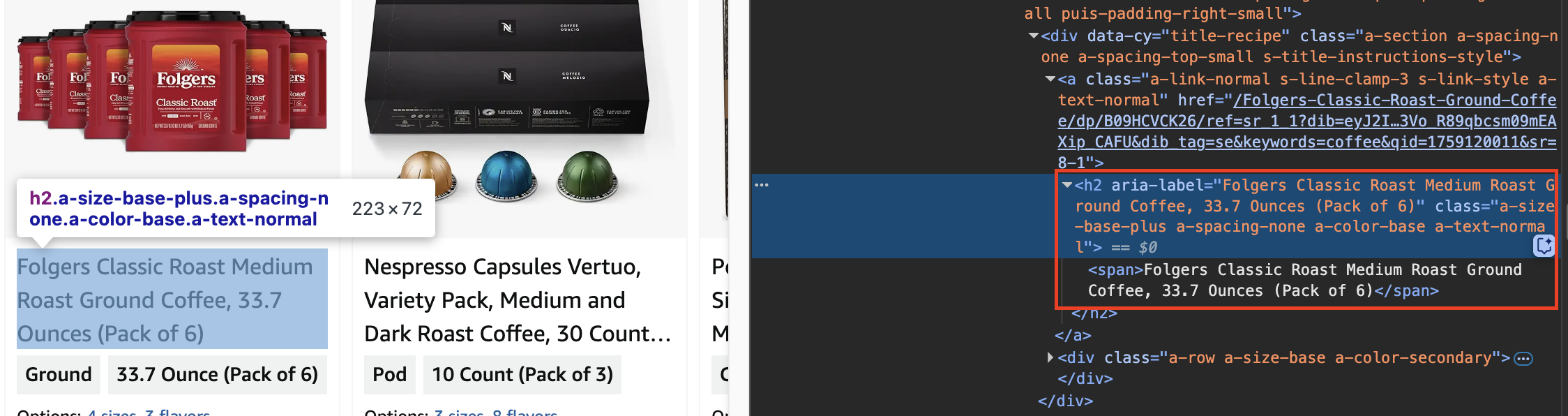
product_name = container.find('h2').get_text(strip=True)
print("Product Name:", product_name)
Scrape "Star Ratings" and "Number of Ratings"
Both of these values are inside the same review block.
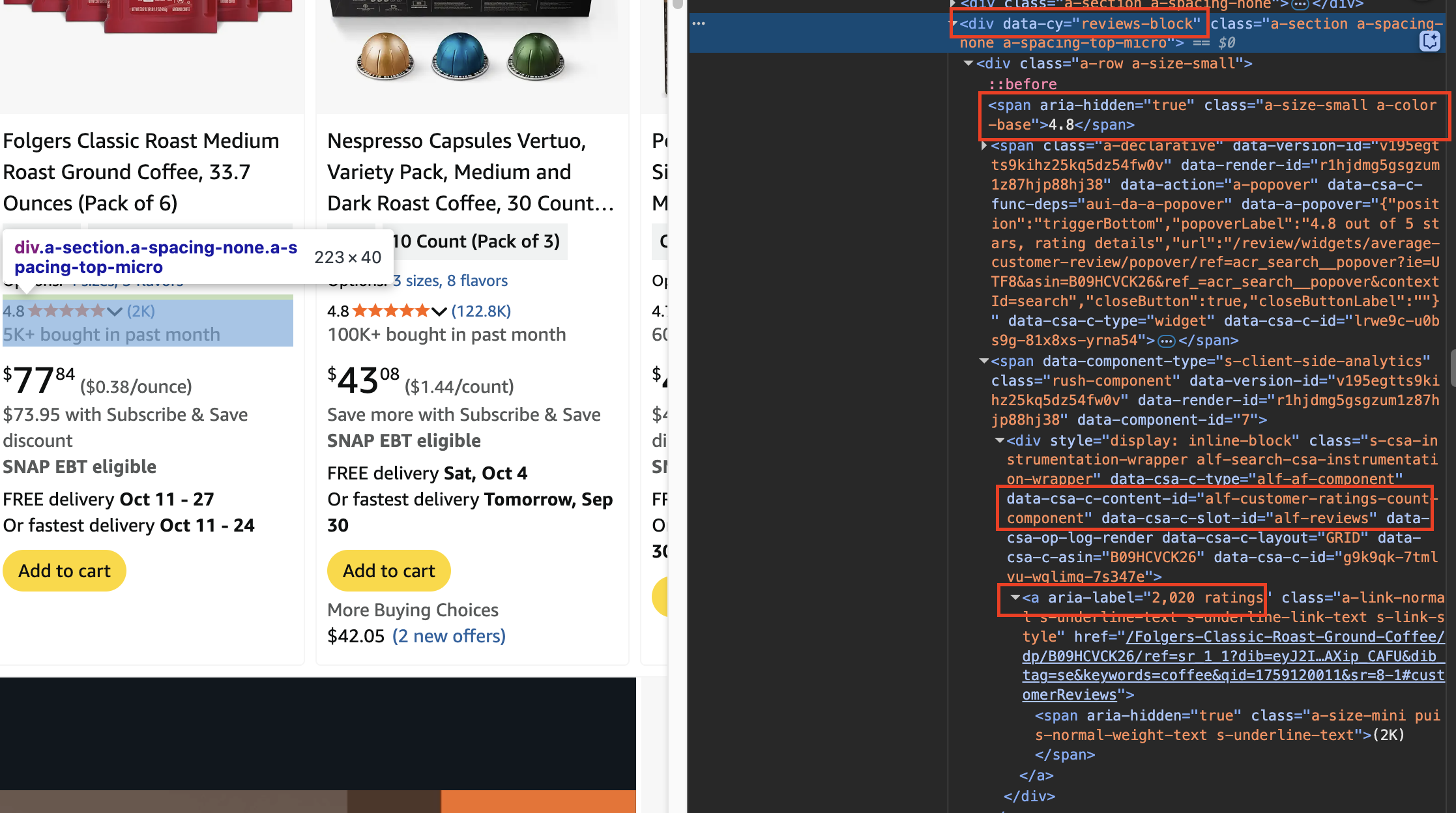
review_block = container.find('div', {'data-cy': 'reviews-block'})star_rating = review_block.find('span', {'class': 'a-size-small'}).get_text(strip=True)
number_of_reviews = review_block.find('div', {'data-csa-c-content-id': 'alf-customer-ratings-count-component'}).find('a').get('aria-label')
print("Star Rating:", star_rating, "stars")
print("Number of Ratings:", number_of_reviews)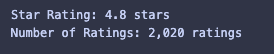
Scrape "Price"
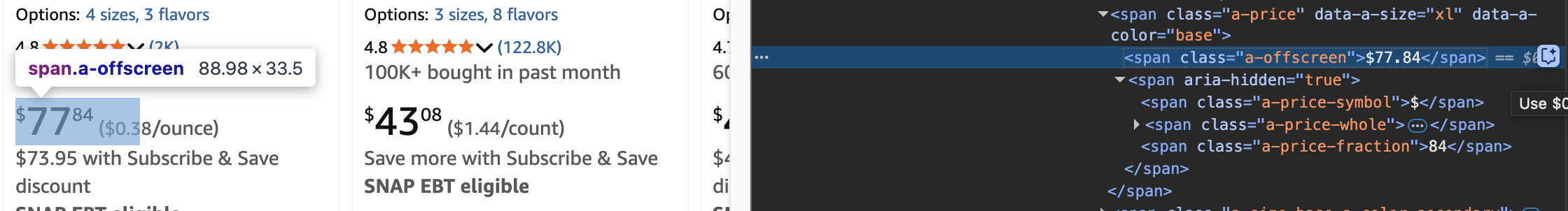
price = container.find('span', {'class': 'a-offscreen'}).get_text(strip=True)
print("Price: $", price)
Step 4: Loops through all the elements and saves the Data
To save all the products from the first page, we can loop through the product_containers and use pandas to convert the data into a structured CSV file.
def extract_all_products():
products = []
for container in product_containers:
product = {}
# Extract Product Name
name_element = container.find('h2')
if name_element:
product['product_name'] = name_element.get_text(strip=True)
else:
product['product_name'] = 'N/A'
# Extract Stars Rating and Number of Reviews
review_block = container.find('div', {'data-cy': 'reviews-block'})
if review_block:
# Extract star rating
star_rating_element = review_block.find('span', {'class': 'a-size-small'})
if star_rating_element:
rating_text = star_rating_element.get_text(strip=True)
rating_match = re.search(r'(\d+\.?\d*)', rating_text)
product['star_rating'] = rating_match.group(1) if rating_match else 'N/A'
else:
product['star_rating'] = 'N/A'
# Extract number of reviews
reviews_element = review_block.find('div', {'data-csa-c-content-id': 'alf-customer-ratings-count-component'})
if reviews_element:
reviews_link = reviews_element.find('a')
if reviews_link:
reviews_text = reviews_link.get('aria-label', '')
reviews_match = re.search(r'([\d,]+)', reviews_text)
product['num_rating'] = reviews_match.group(1) if reviews_match else 'N/A'
else:
product['num_rating'] = 'N/A'
else:
product['num_rating'] = 'N/A'
else:
product['star_rating'] = 'N/A'
product['num_rating'] = 'N/A'
# Extract Price
price_element = container.find('span', {'class': 'a-offscreen'})
if price_element:
price_text = price_element.get_text(strip=True)
# Clean up the price text (remove extra $ symbols)
price_clean = price_text.replace('$', '').strip()
product['price'] = price_clean if price_clean else 'N/A'
else:
product['price'] = 'N/A'
# Only add products that have at least a name
if product['product_name'] != 'N/A':
products.append(product)
return products
def save_to_csv(products, filename='amazon_products.csv'):
"""Save products data to CSV file"""
if not products:
print("No products to save!")
return
# Define CSV fieldnames
fieldnames = ['product_name', 'star_rating', 'num_rating', 'price']
with open(filename, 'w', newline='', encoding='utf-8') as csvfile:
writer = csv.DictWriter(csvfile, fieldnames=fieldnames)
writer.writeheader()
writer.writerows(products)
print(f"Data saved to {filename}")
# Extract all products
all_products = extract_all_products()
# Save to CSV
save_to_csv(all_products)
# Display results
print(f"Found {len(all_products)} products:")
print("=" * 80)
for i, product in enumerate(all_products, 1):
print(f"{i}. {product['product_name']}")
print(f" Star Rating: {product['star_rating']} stars")
print(f" Number of Ratings: {product['num_rating']}")
print(f" Price: ${product['price']}")
print("-" * 80)
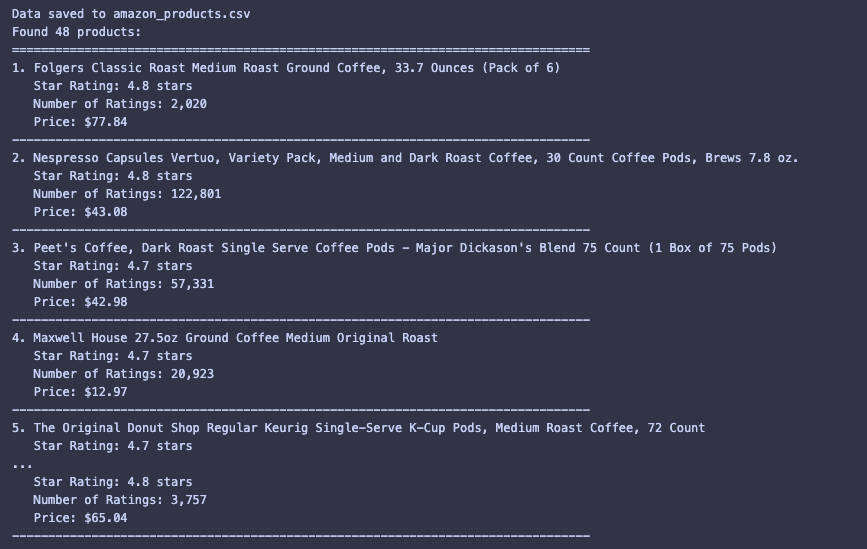
And you can also find the CSV file in your directory. All the source code is available in this github repo.
Next Steps
You can try scraping the other parameters using the same steps we showed. However, keep in mind that Amazon actively blocks scraping bots. So, methods that work today may not work tomorrow. Also, we only scrape part of the data, but using our Amazon Search API gives a more complete data set.
API: Amazon Search API (Recommended)
You can scrape this data with a straightforward GET request using our new Amazon Search Engine Results API.
We'll show you how to scrape both the search results and the individual product pages.

Available data on the Amazon Search API
Here is the list of data you can retrieve from this Amazon Search API:
- product ads (when available)
- organic results
- video results
- related searches
- sponsored brands
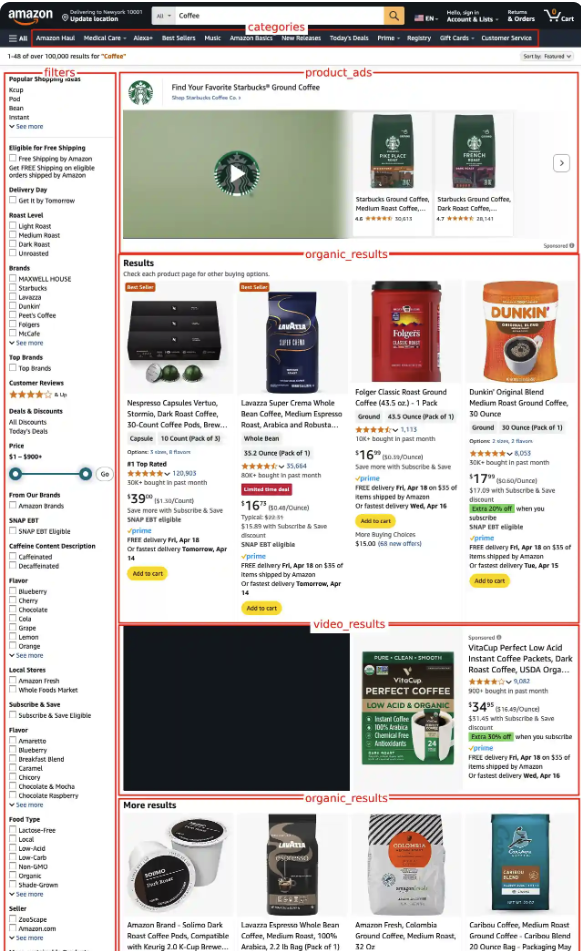
The organic_results will include information like:
- position
- ASIN (Amazon Standard Identification Number)
- badges
- title
- link
- thumbnail
- rating
- reviews
- price
- offers
- and more!
This is perfect if you need to collect product data from Amazon. It's also useful if you're looking to monitor your competitor's products at an online store like Amazon.
How to scrape Amazon Search results?
Now, let's see how to use this simple API from SerpApi to collect the data!

Get your API Key
First, ensure to register at serpapi.com to get your API Key. You can get 100 free searches per month. You can use this API Key to access all of our APIs, including the Amazon Search API.
Available parameters
On top of running the basic search, you can see all of our available parameters here.
Video Tutorial
We also have a video tutorial on scraping Amazon on YouTube:
cURL Implementation
Here is the basic implementation in cURL:
curl --get https://serpapi.com/search \
-d api_key="YOUR_API_KEY" \
-d engine="amazon" \
-d k="Coffee"The k parameter is responsible for the search query.
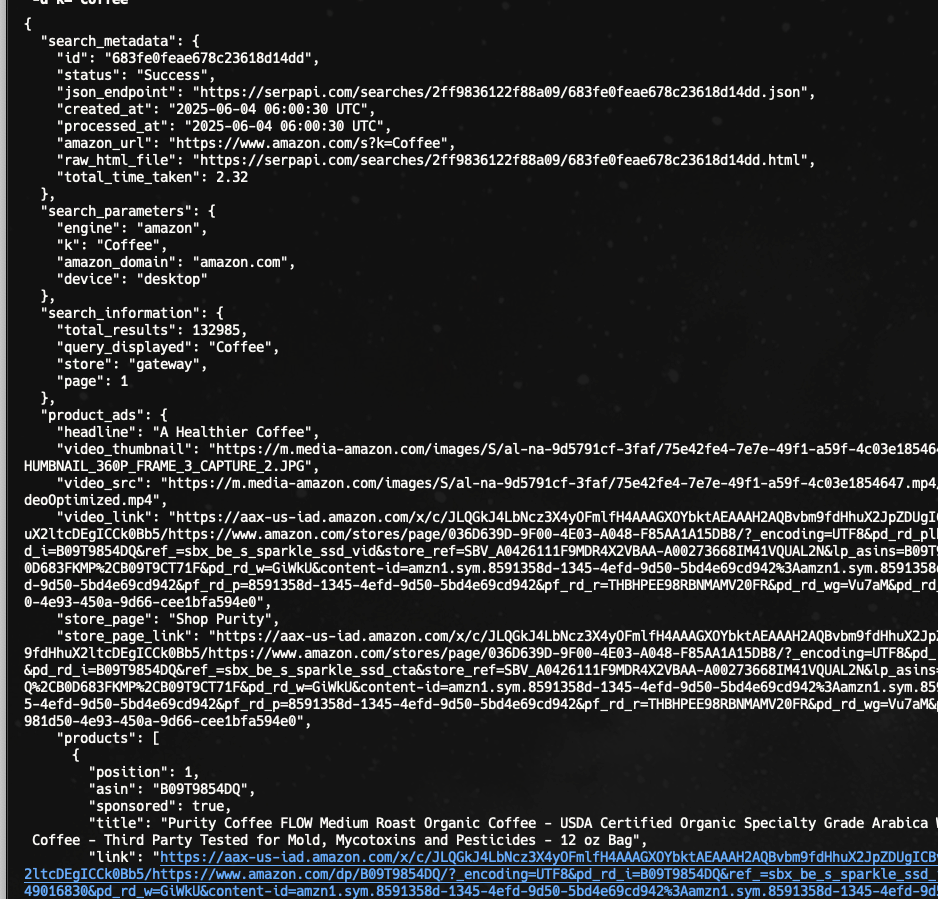
Python Implementation
Next, let's see how to scrape the Amazon search results in Python.
Preparation for accessing the SerpApi API in Python
- Create a new
main.pyfile - Install requests with:
pip install requestsHere is what the basic setup looks like:
import requests
SERPAPI_API_KEY = "YOUR_REAL_SERPAPI_API_KEY"
params = {
"api_key": SERPAPI_API_KEY, #replace with your real API Key
# soon
}
search = requests.get("https://serpapi.com/search", params=params)
response = search.json()
print(response)With these few lines of code, we can access all of the search engines available at SerpApi, including the Amazon Search API.
import requests
SERPAPI_API_KEY = "YOUR_SERPAPI_API_KEY"
params = {
"api_key": SERPAPI_API_KEY,
"engine": "amazon",
"k": "Coffee"
}
search = requests.get("https://serpapi.com/search", params=params)
response = search.json()
print(response)To make it easier to see the response, let's add indentation.
import json
# ...
# ...
# all previous code
print(json.dumps(response, indent=2))Print specific information
Let's say we only need the title, ASIN, thumbnail, price, rating, reviews, and link; This is how we can print specific columns from the organic results:
# ...
search = requests.get("https://serpapi.com/search", params=params)
response = search.json()
for result in response.get("organic_results", []):
title = result.get("title")
asin = result.get("asin")
thumbnail = result.get("thumbnail")
price = result.get("price")
rating = result.get("rating")
reviews = result.get("reviews")
link = result.get("link")
print(f"Title: {title}")
print(f"ASIN: {asin}")
print(f"Thumbnail: {thumbnail}")
print(f"Price: {price}")
print(f"Rating: {rating}")
print(f"Reviews: {reviews}")
print(f"Link: {link}")
print("-" * 10)Scrape Amazon Product ASINs
ASIN stands for Amazon Standard Identification Number, a 10-character alphanumeric code that Amazon uses to identify products. You can collect these ASIN numbers by looping through the search results.
Scrape Amazon Product prices
Same with the ASIN number, you can also loop through the search results to collect prices information from each of the items.
Export data to a CSV file
Let's see how to export this Amazon product data into a CSV file in Python
import csv
with open("amazon_results.csv", "w", newline="", encoding="utf-8") as csvfile:
fieldnames = ["title", "asin", "thumbnail", "price", "rating", "reviews", "link"]
writer = csv.DictWriter(csvfile, fieldnames=fieldnames)
writer.writeheader()
for result in response.get("organic_results", []):
writer.writerow({
"title": result.get("title"),
"asin": result.get("asin"),
"thumbnail": result.get("thumbnail"),
"price": result.get("price"),
"rating": result.get("rating"),
"reviews": result.get("reviews"),
"link": result.get("link")
})
print("Data exported to amazon_results.csv successfully.")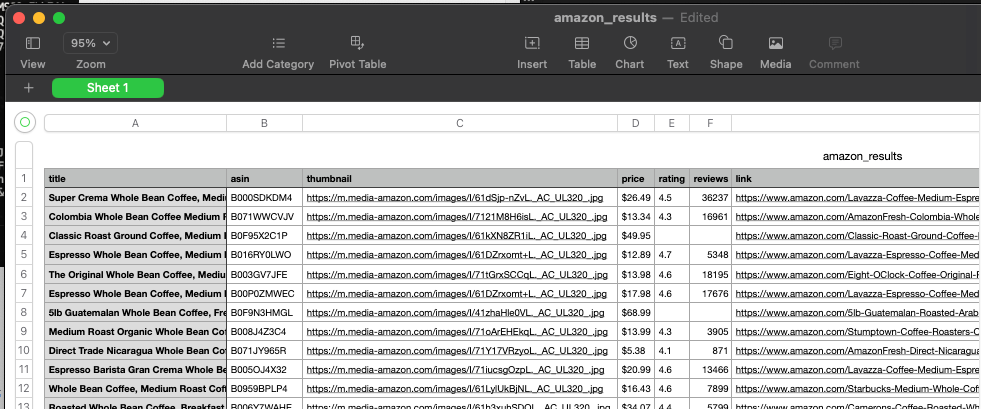
JavaScript implementation
Finally, let's see how to scrape the Amazon search results in JavaScript.
Install the serpapi package:
npm install serpapiRun a basic query:
const { getJson } = require("serpapi");
getJson({
engine: "amazon",
api_key: API_KEY, // Put your API Key
k: "coffee"
}, (json) => {
console.log(json["organic_results"]);
});More information on our JavaScript library: GitHub - SerpApi-javascript
Other programming languages
While you can use our APIs using a simple GET request with any programming language, you can also see our ready-to-use libraries here: SerpApi Integrations.
How to customize the search?
We provide many filters to customize or filter your programmatic search.
Localize the results:
You can localize the results by adjusting the amazon_domain and language parameter.
- amazon_domain: Parameter defines the Amazon domain to use. It defaults to
amazon.com. Head to Amazon domains for a full list of supported Amazon domains. - language: Parameter defines the language to use for the Amazon search. It's a locale name represented as <language>_<REGION>. (e.g., on amazon.com
en_USfor English,es_USfor Spanish, or on amazon.co.jpja_JPfor Japanese). Head to the following page for a complete list of supported Amazon languages.
Example using a different Amazon domain:
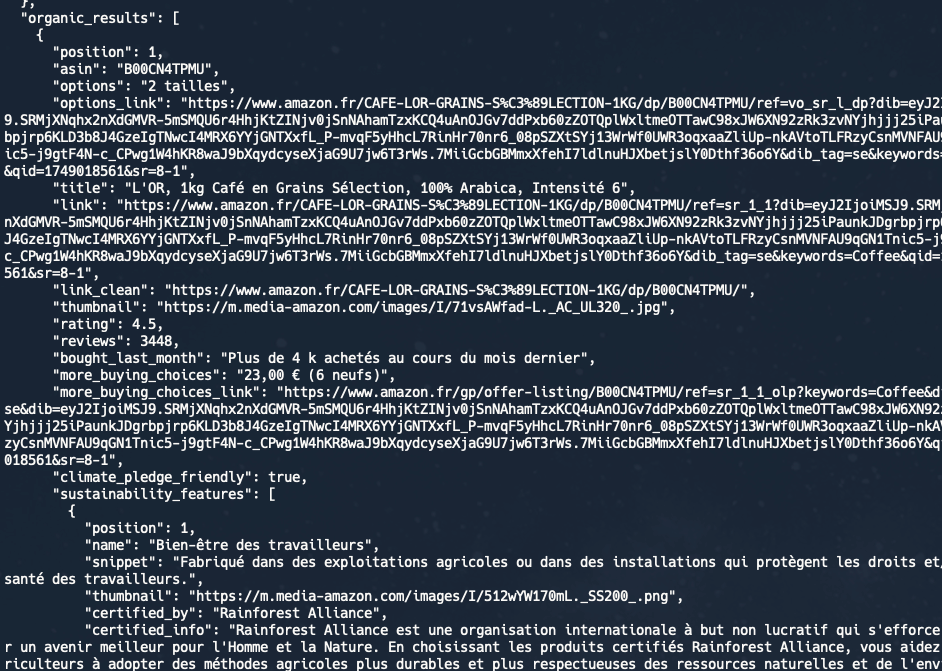
curl --get https://serpapi.com/search \
-d api_key="YOUR_API_KEY" \
-d engine="amazon" \
-d k="Coffee" \
-d amazon_domain="amazon.fr"As you can see, the results are now returned from Amazon French:
Advanced Parameters:
- delivery_zip: ZIP Postal code. To filter the shipping products by a selected area.
- shipping_location: Shipping country. To filter the shipping products by a selected country.
- s: Parameter is used to sort results. Available options:
relevanceblender - Featured (default)price-asc-rank - Price: Low to Highprice-desc-rank - Price: High to Lowreview-rank - Avg. Customer Reviewdate-desc-rank - Newest Arrivalsexact-aware-popularity-rank - Best Sellers
You can see more of the available parameters on this documentation page.
How to paginate the results?
You can scrape beyond the first page using the page parameter. The default value is 1 for the page result. You can then increase it by one for the next pages.2 for the 2nd page of results, 3 for the 3rd page of results, etc..
How to scrape Amazon Product Data?
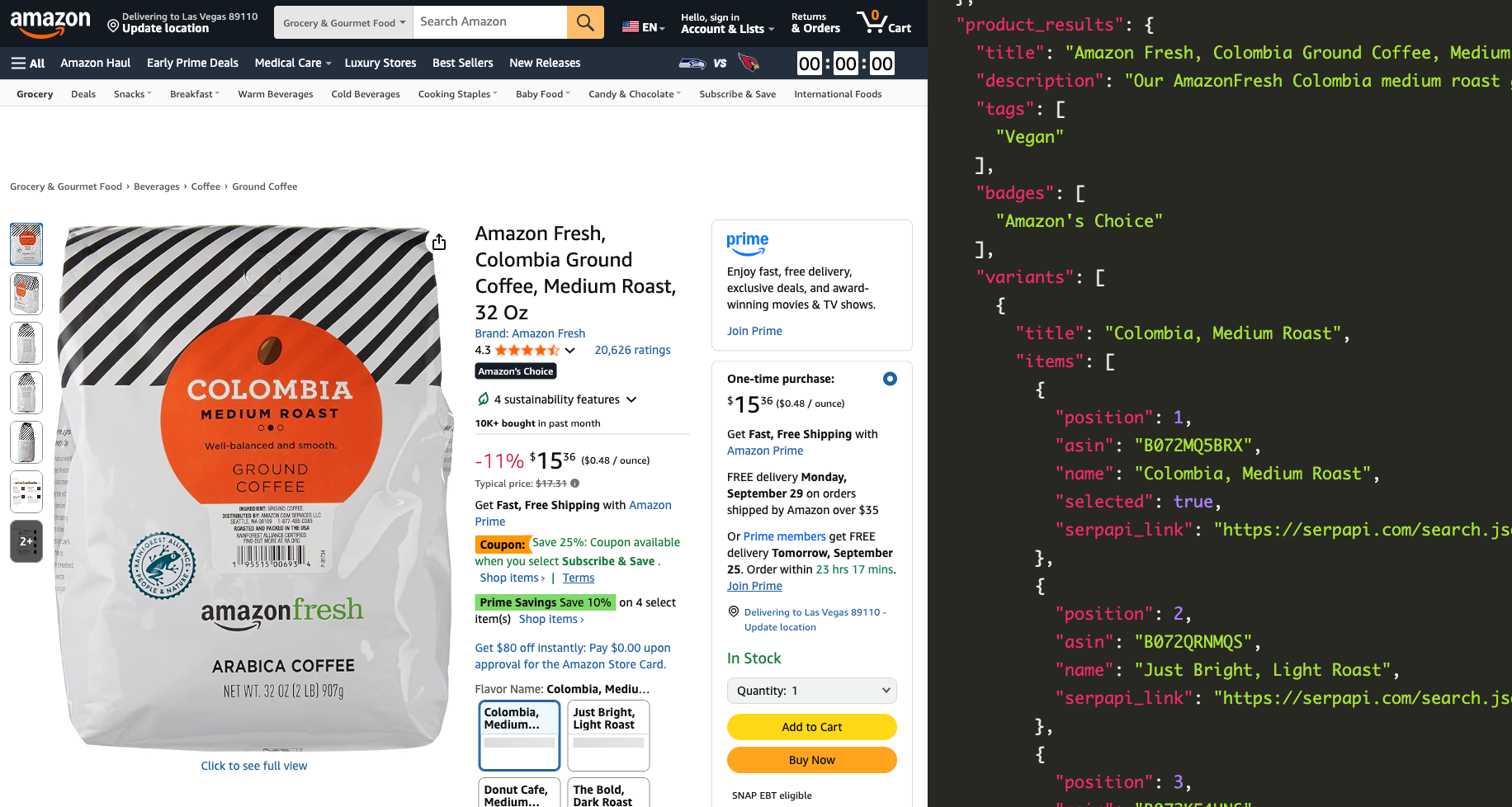
We've seen how to scrape the search results. Next, let's see how to scrape the individual page, simulating when you click one of the products using our Amazon Product API.
Video Tutorial
Python example
Here is the parameter we need to use:
import requests
SERPAPI_API_KEY = "YOUR_SERPAPI_API_KEY"
params = {
"engine": "amazon_product",
"asin": "B072MQ5BRX",
"api_key": "API_KEY"
}
search = requests.get("https://serpapi.com/search", params=params)
response = search.json()
print(response)engine:The engine needs to be amazon_productasin:Use ASIN of the product you interested in.
Available Product Information
We return:
- Basic product information
- Variants
- Thumbnail links
- Item specifications
- Frequently bought together items
- Related products (complete with their ASIN numbers)
- Sponsored brands
- Reviews information
Scrape reviews from an Amazon Product
Let's see how to collect public reviews from a product
import requests
SERPAPI_API_KEY = "YOUR_SERPAPI_API_KEY"
params = {
"engine": "amazon_product",
"asin": "B072MQ5BRX",
"api_key": "API_KEY"
}
search = requests.get("https://serpapi.com/search", params=params)
response = search.json()
print(response["reviews_information"]["authors_reviews"])Or, if you want to get a specific item from the reviews, let's say title, text, date, and rating:
for review in response["reviews_information"]["authors_reviews"]:
print("Title:", review["title"])
print("Text:", review["text"])
print("Date:", review["date"])
print("Rating:", review["rating"])
print("==========================\n")Result example:

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Is it legal to scrape the Amazon website?
Scraping publicly available data from websites like Amazon is generally permitted under U.S. law.
How much does it cost?
Register at serpapi.com to start for free. If you want to scale, we offer tiered plans based on your usage.
Why do you need to scrape Amazon product data?
Scraping Amazon product data can provide valuable insights for businesses and individuals looking to enhance their competitive edge and inform decision-making. It allows for effective price monitoring, enabling companies to track price changes over time, adjust their pricing strategies, and implement dynamic pricing to stay competitive in the marketplace.
Additionally, it facilitates comprehensive market research by gathering data on competitor products, reviews, ratings, and sales ranks, which helps understand market trends and customer preferences. Scraping data can also improve inventory management by monitoring stock levels and availability. For consumers and businesses alike, it aids in product comparison, keyword research for visibility optimization, and review analysis to identify common issues and customer sentiment.
Moreover, it can assist in estimating sales volume and generating leads for potential products to promote.
Closing
That's it! Thank you very much for reading this blog post. You can play around for free on our playground here.
If you need other resources to collect more data on a product or monitor prices, please check our other awesome APIs:



