What will be scraped

Google Scholar Organic Results API
Alternatively, you can use the Google Scholar Organic Results API from SerpApi. SerpApi is a free API with 100 searches per month. If you need more searches, there are paid plans.
The difference is that you won't have to write code from scratch and maintain it. You may also experience blocking from Google and changing the selected selectors. Using a ready-made solution from SerpAPI, you just need to iterate the received JSON. Check out the playground.
First we need to install google-search-results-nodejs. To do this you need to enter in your console: npm i google-search-results-nodejs
const SerpApi = require("google-search-results-nodejs");
const search = new SerpApi.GoogleSearch(process.env.API_KEY); //your API key from serpapi.com
const searchString = "artificial intelligence"; // what we want to search
const params = {
engine: "google_scholar", // search engine
q: searchString, // search query
hl: "en", // Parameter defines the language to use for the Google search
};
const getScholarData = function ({ organic_results }) {
return organic_results.map((result) => {
const { title, link = "link not available", snippet, publication_info, inline_links, resources } = result;
return {
title,
link,
publication_info: publication_info?.summary,
snippet,
document: resources?.map((el) => el.link)[0] || "document not available",
cited_by: inline_links?.cited_by?.link || "link not available",
related_articles: inline_links?.related_pages_link || "link not available",
all_versions: inline_links?.versions?.link || "link not available",
};
});
};
const getJson = (params) => {
return new Promise((resolve) => {
search.json(params, resolve);
})
}
getJson(params).then(getScholarData).then(console.log)
Code explanation
Declare constants from required libraries:
const SerpApi = require("google-search-results-nodejs");
const search = new SerpApi.GoogleSearch(API_KEY);
| Code | Explanation |
|---|---|
SerpApi |
SerpApi Node.js library |
search |
new instance of GoogleSearch class |
API_KEY |
your API key from SerpApi |
Next, we write down what we want to search and the necessary parameters for making a request:
const searchString = "artificial intelligence";
const params = {
engine: "google_scholar",
q: searchString,
hl: "en",
};
| Code | Explanation |
|---|---|
searchString |
what we want to search |
engine |
search engine |
q |
search query |
hl |
parameter defines the language to use for the Google search |
Next, we write a callback function in which we describe what data we need from the result of our request:
const getScholarData = function ({ organic_results }) {
return organic_results.map((result) => {
const { title, link = "link not available", snippet, publication_info, inline_links, resources } = result;
return {
title,
link,
publication_info: publication_info?.summary,
snippet,
document: resources?.map((el) => el.link)[0] || "document not available",
cited_by: inline_links?.cited_by?.link || "link not available",
related_articles: inline_links?.related_pages_link || "link not available",
all_versions: inline_links?.versions?.link || "link not available",
};
});
};
| Code | Explanation |
|---|---|
organic_results |
an array that we destructured from response |
title, link, snippet, ..., resources |
data that we destructured from element of organic_results array |
link = "link not available" |
we set default value link not available if link is undefined |
Next, we wrap the search method from the SerpApi library in a promise to further work with the search results and run it:
const getJson = (params) => {
return new Promise((resolve) => {
search.json(params, resolve);
})
}
getJson(params).then(getKnowledgeGraph).then(console.log)
Output
[
{
"title":"[HTML][HTML] Artificial intelligence and algorithmic bias: implications for health systems",
"link":"https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/pmc6875681/",
"publication_info":"T Panch, H Mattie, R Atun - Journal of global health, 2019 - ncbi.nlm.nih.gov",
"snippet":"A consumer study of an image search on a popular search engine revealed that 11% of results for the term “CEO” were female [6]. At the time, 20% of CEO’s in the US were women [7]. …",
"document":"https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/pmc6875681/",
"cited_by":"http://scholar.google.com/scholar?cites=2905556560707838221&as_sdt=2005&sciodt=0,5&hl=en",
"related_articles":"http://scholar.google.com/scholar?q=related:DeHLM0ycUigJ:scholar.google.com/&scioq=artificial%2520intelligence&hl=en&as_sdt=0,5",
"all_versions":"http://scholar.google.com/scholar?cluster=2905556560707838221&hl=en&as_sdt=0,5"
},
{
"title":"[PDF][PDF] The impact of artificial intelligence on international trade",
"link":"https://www.hinrichfoundation.com/media/2bxltgzf/meltzerai-and-trade_final.pdf",
"publication_info":"JP Meltzer - Brookings Institute, 2018 - hinrichfoundation.com",
"snippet":"Artificial intelligence (AI) stands to have a transformative impact on international trade. Already, specific applications in areas such as data analytics and translation services are …",
"document":"https://www.hinrichfoundation.com/media/2bxltgzf/meltzerai-and-trade_final.pdf",
"cited_by":"http://scholar.google.com/scholar?cites=7020069348513013331&as_sdt=2005&sciodt=0,5&hl=en",
"related_articles":"http://scholar.google.com/scholar?q=related:U9656OBLbGEJ:scholar.google.com/&scioq=artificial%2520intelligence&hl=en&as_sdt=0,5",
"all_versions":"http://scholar.google.com/scholar?cluster=7020069348513013331&hl=en&as_sdt=0,5"
},
...and other results
]
DIY Preparation
First, we need to create a Node.js* project and add npm packages cheerio to parse parts of the HTML markup, and axios to make a request to a website. To do this, in the directory with our project, open the command line and enter npm init -y, and then npm i cheerio axios.
*If you don't have Node.js installed, you can download it from nodejs.org and follow the installation documentation.
Process
SelectorGadget Chrome extension was used to grab CSS selectors by clicking on the desired element in the browser. If you have any struggles understanding this, we have a dedicated Web Scraping with CSS Selectors blog post at SerpApi.
The Gif below illustrates the approach of selecting different parts of the results.
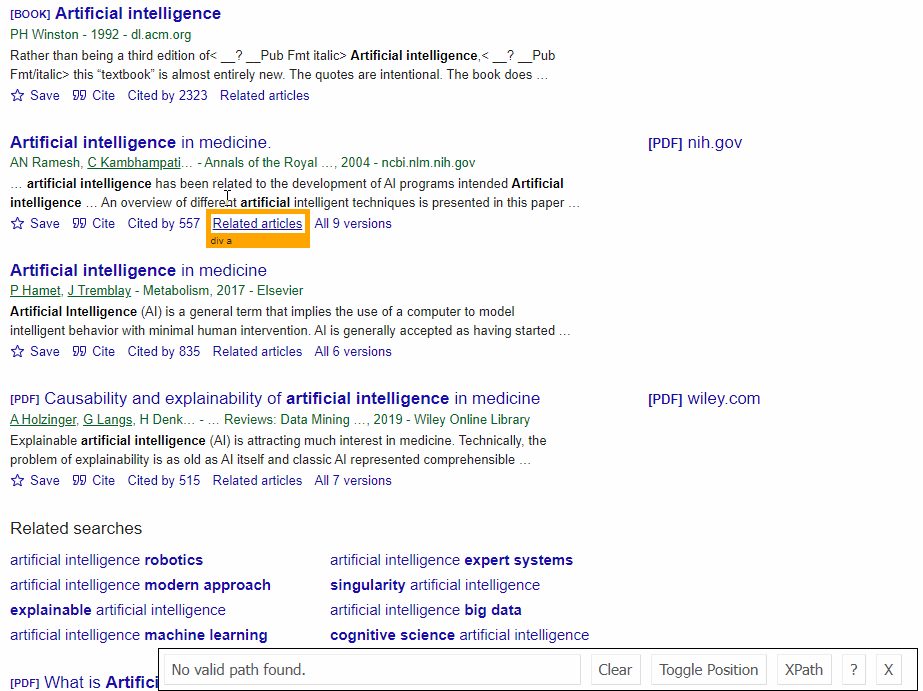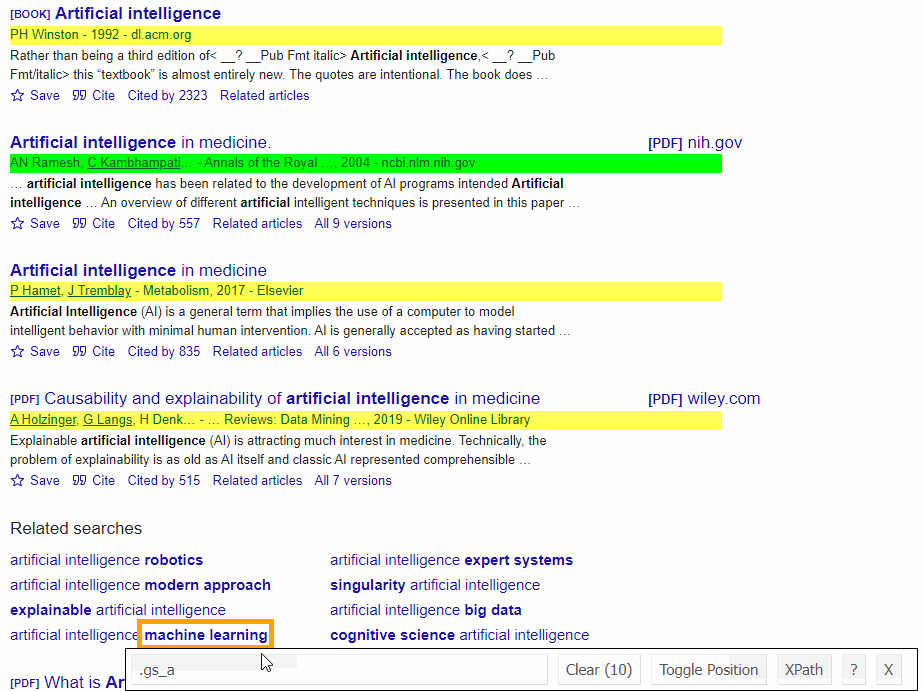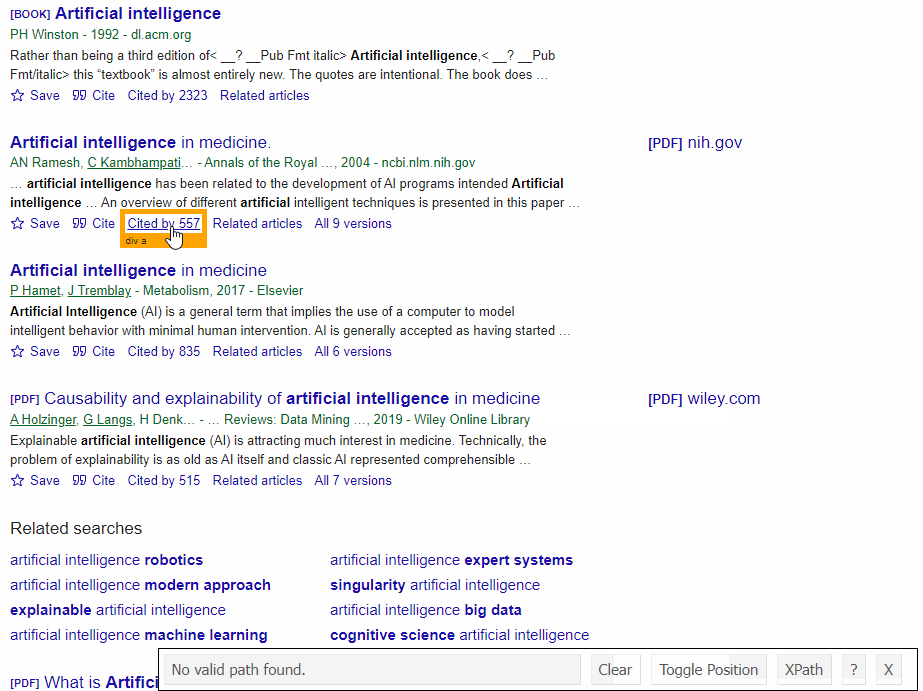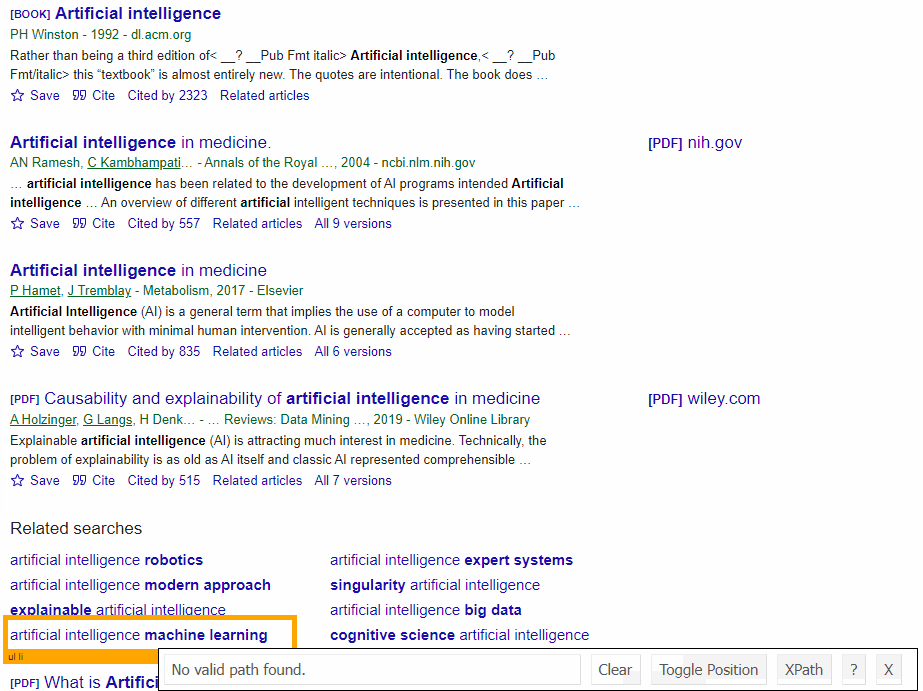
DIY Code
const cheerio = require("cheerio");
const axios = require("axios");
const searchString = "artificial intelligence"; // what we want to search
const encodedString = encodeURI(searchString); // what we want to search for in URI encoding
const domain = `http://scholar.google.com`;
const AXIOS_OPTIONS = {
headers: {
"User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/101.0.4951.64 Safari/537.36",
}, // adding the User-Agent header as one way to prevent the request from being blocked
params: {
q: encodedString, // our encoded search string
hl: "en", // parameter defines the language to use for the Google search
},
};
function buildValidLink(rawLink) {
if (!rawLink || rawLink.includes("javascript:void(0)")) return "link not available";
if (rawLink.includes("scholar.googleusercontent")) return rawLink;
return domain + rawLink;
}
function getScholarOrganicResults() {
return axios.get(`${domain}/scholar`, AXIOS_OPTIONS).then(function ({ data }) {
let $ = cheerio.load(data);
const organicResults = Array.from($(".gs_r.gs_scl")).map((el) => {
const cited_by_rawLink = $(el).find(".gs_fl > a:nth-child(3)").attr("href");
const related_articles_rawLink = $(el).find(".gs_fl > a:nth-child(4)").attr("href");
const all_versions_rawLink = $(el).find(".gs_fl > a:nth-child(5)").attr("href");
const cited_by = buildValidLink(cited_by_rawLink);
const related_articles = buildValidLink(related_articles_rawLink);
const all_versions = buildValidLink(all_versions_rawLink);
return {
title: $(el).find(".gs_rt").text().trim(),
link: $(el).find(".gs_rt a").attr("href") || "link not available",
publication_info: $(el).find(".gs_a").text().trim(),
snippet: $(el).find(".gs_rs").text().trim().replace("\n", ""),
document: $(el).find(".gs_or_ggsm a").attr("href") || "document not available",
cited_by,
related_articles,
all_versions,
};
});
return organicResults;
});
}
getScholarOrganicResults().then(console.log);
Code explanation
Declare constants from required libraries:
const cheerio = require("cheerio");
const axios = require("axios");
| Code | Explanation |
|---|---|
cheerio |
library for parsing the html page and access the necessary selectors |
axios |
library for requesting the desired html document |
Next, we write in constants what we want to search for and encode our text into a URI string:
const searchString = "artificial intelligence";
const encodedString = encodeURI(searchString);
| Code | Explanation |
|---|---|
searchString |
what we want to search |
encodedString |
what we want to search for in URI encoding |
Next, we write down the necessary parameters for making a request:
const AXIOS_OPTIONS = {
headers: {
"User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/101.0.4951.64 Safari/537.36",
},
params: {
q: encodedString,
hl: "en",
},
};
| Code | Explanation |
|---|---|
headers |
HTTP headers let the client and the server pass additional information with an HTTP request or response |
User-Agent |
is used to act as a "real" user visit. Default axios requests user-agent is axios/0.27.2 so websites understand that it's a script that sends a request and might block it. Check what's your user-agent. |
q |
encoded in URI search query |
hl |
parameter defines the language to use for the Google search |
Next, we write a function that helps us change the raw links to the correct links:
function buildValidLink(rawLink) {
if (!rawLink || rawLink.includes("javascript:void(0)")) return "link not available";
if (rawLink.includes("scholar.googleusercontent")) return rawLink;
return domain + rawLink;
}
We need to do this with links because they are of different types. For example, some links start with "/scholar", some already have a complete and correct link, and some no links.
And finally a function to get the necessary information:
function getScholarInfo() {
return axios.get(`${domain}/scholar`, AXIOS_OPTIONS).then(function ({ data }) {
let $ = cheerio.load(data);
const organicResults = Array.from($(".gs_r.gs_scl")).map((el) => {
const cited_by_rawLink = $(el).find(".gs_fl > a:nth-child(3)").attr("href");
const related_articles_rawLink = $(el).find(".gs_fl > a:nth-child(4)").attr("href");
const all_versions_rawLink = $(el).find(".gs_fl > a:nth-child(5)").attr("href");
const cited_by = buildValidLink(cited_by_rawLink);
const related_articles = buildValidLink(related_articles_rawLink);
const all_versions = buildValidLink(all_versions_rawLink);
return {
title: $(el).find(".gs_rt").text().trim(),
link: $(el).find(".gs_rt a").attr("href") || "link not available",
publication_info: $(el).find(".gs_a").text().trim(),
snippet: $(el).find(".gs_rs").text().trim().replace("\n", ""),
document: $(el).find(".gs_or_ggsm a").attr("href") || "document not available",
cited_by,
related_articles,
all_versions,
};
});
return organicResults;
});
}
| Code | Explanation |
|---|---|
function ({ data }) |
we received the response from axios request that have data key that we destructured (this entry is equal to function (response) and in the next line cheerio.load(response.data)) |
organicResults |
an array with organic results from page |
.attr('href') |
gets the href attribute value of the html element |
$(el).find('.gs_rt') |
finds element with class name gs_rt in all child elements and their children of el html element |
.text() |
gets the raw text of html element |
.trim() |
removes whitespace from both ends of a string |
replace('\n', '') |
in this code we remove new line symbol |
Now we can launch our parser. To do this enter node YOUR_FILE_NAME in your command line. Where YOUR_FILE_NAME is the name of your .js file.
Output
[
{
"title":"[HTML][HTML] Artificial intelligence and algorithmic bias: implications for health systems",
"link":"https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/pmc6875681/",
"publication_info":"T Panch, H Mattie, R Atun - Journal of global health, 2019 - ncbi.nlm.nih.gov",
"snippet":"A consumer study of an image search on a popular search engine revealed that 11% of results for the term “CEO” were female [6]. At the time, 20% of CEO’s in the US were women [7]. …",
"document":"https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/pmc6875681/",
"cited_by":"http://scholar.google.com/scholar?cites=2905556560707838221&as_sdt=2005&sciodt=0,5&hl=en",
"related_articles":"http://scholar.google.com/scholar?q=related:DeHLM0ycUigJ:scholar.google.com/&scioq=artificial%2520intelligence&hl=en&as_sdt=0,5",
"all_versions":"http://scholar.google.com/scholar?cluster=2905556560707838221&hl=en&as_sdt=0,5"
},
{
"title":"[PDF][PDF] The impact of artificial intelligence on international trade",
"link":"https://www.hinrichfoundation.com/media/2bxltgzf/meltzerai-and-trade_final.pdf",
"publication_info":"JP Meltzer - Brookings Institute, 2018 - hinrichfoundation.com",
"snippet":"Artificial intelligence (AI) stands to have a transformative impact on international trade. Already, specific applications in areas such as data analytics and translation services are …",
"document":"https://www.hinrichfoundation.com/media/2bxltgzf/meltzerai-and-trade_final.pdf",
"cited_by":"http://scholar.google.com/scholar?cites=7020069348513013331&as_sdt=2005&sciodt=0,5&hl=en",
"related_articles":"http://scholar.google.com/scholar?q=related:U9656OBLbGEJ:scholar.google.com/&scioq=artificial%2520intelligence&hl=en&as_sdt=0,5",
"all_versions":"http://scholar.google.com/scholar?cluster=7020069348513013331&hl=en&as_sdt=0,5"
},
...and other results
]
Links
If you want to see some projects made with SerpApi, please write me a message.
Add a Feature Request💫 or a Bug🐞
