In the world of e-commerce, eBay is one of the largest online marketplaces, alongside Amazon, Walmart, Etsy, Alibaba, and Rakuten. Scraping eBay search results provides significant value to businesses, researchers, and consumers by supporting market research and competitor analysis, pricing intelligence, product research and development, consumer insights, and enhanced buying decisions.
This tutorial will walk you through how to:
- Scrape eBay listings and prices from search results (titles, links, thumbnails, seller usernames, review counts, and more).
- Scrape eBay reviews using the eBay Product API.
Let's dive in!
Challenges of Scraping eBay Manually
Scraping eBay search results may look simple at first, but doing it consistently, especially at scale, is difficult. Developers often face:
- CAPTCHA and bot detection.
- IP blocking and rate limits.
- Session timeouts.
- Dynamic and frequently changing HTML structure.
- Pagination and infinite scrolling.
- Data variability and missing fields.
- Legal and ethical constraints.
These issues make DIY scraping slow, fragile, and expensive to maintain over time. You often need browser automation tools like Puppeteer, must constantly search for the right CSS selectors which can break whenever eBay updated its layout, and repeatedly work around anti-bot systens just to keep your scraper alive.
Luckily, instead of tackling these problems manually, SerpApi handles all of this for you and returns clean, ready-to-use structured JSON format.
Setting up a SerpApi account
SerpApi offers 250 free searches every month. You can register a new account and start your first search in our interactive playground directly. When you're ready for more volume, you can review the pricing page.
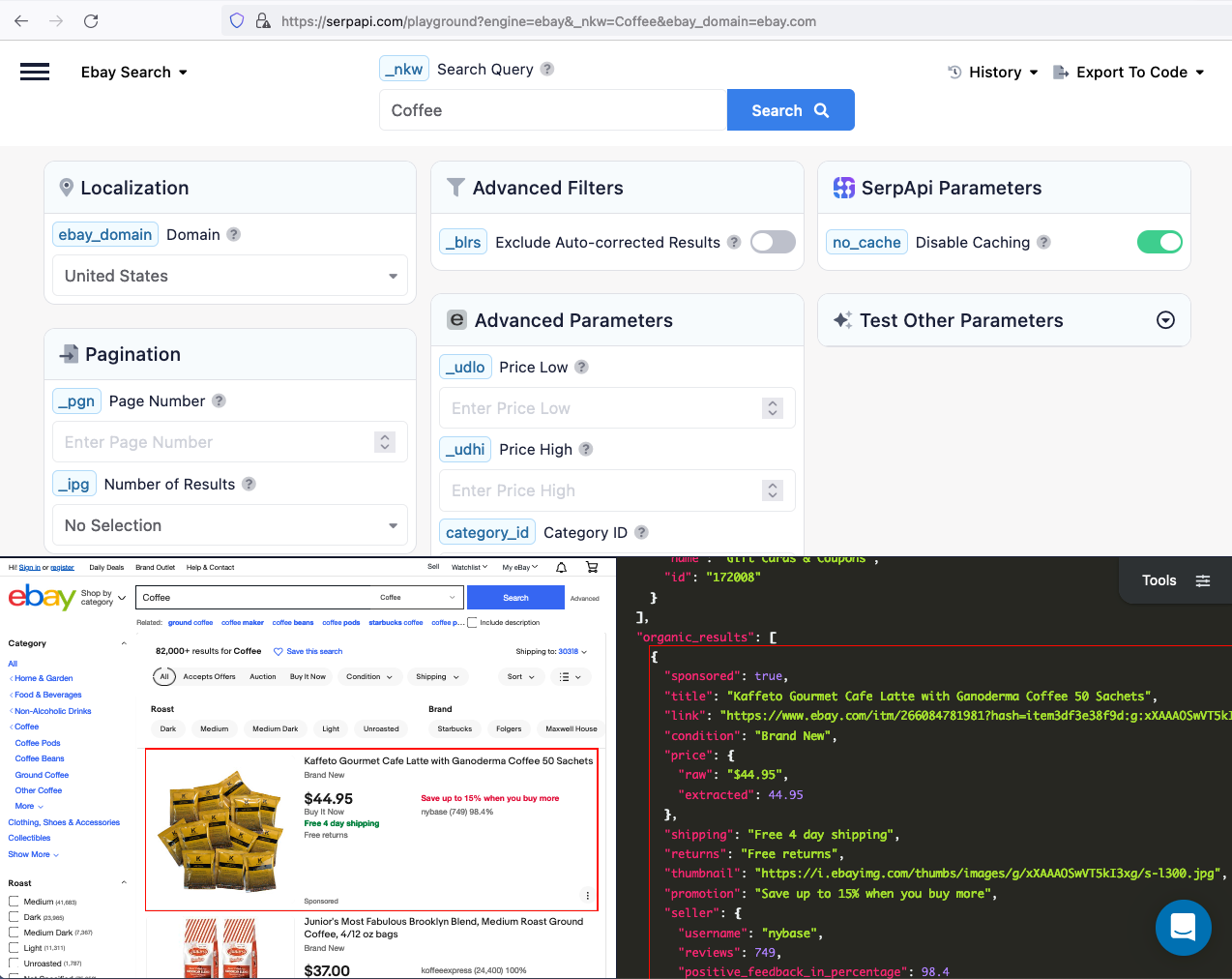
The data we can collect from organic results include: "title", "link", "price", "thumbnail", "promotion", "seller", and more.
Once you are familiar with all the results available, you can start integrating our API into your code.
How to Scrape eBay Listings and Prices from Search Results
Get your API key
First, grab your API key from your dashboard.
JavaScript Tutorial Integration
If you prefer to watch a video, here is the video tutorial on YouTube
First we need to install google-search-results-nodejs. To do this you need to enter in your command line: npm i google-search-results-nodejs
Declare constants from required libraries:
const SerpApi = require("google-search-results-nodejs");
const search = new SerpApi.GoogleSearch(API_KEY);
| Code | Explanation |
|---|---|
SerpApi |
SerpApi Node.js library |
search |
new instance of GoogleSearch class |
API_KEY |
your API key from SerpApi |
Next, we write down what we want to search and the necessary parameters for making a request:
const searchString = "playstation";
const pagesLimit = 10;
let currentPage = 1;
const params = {
engine: "ebay",
_nkw: searchString,
ebay_domain: "ebay.com",
_pgn: currentPage,
};
| Code | Explanation |
|---|---|
searchString |
what we want to search |
pagesLimit |
limit of pages for getting info |
currentPage |
current page of the search |
engine |
search engine |
_nkw |
search query |
ebay_domain |
ebay domain: ebay.com, ebay.de, ebay.co.uk |
_pgn |
current page |
Next, we write a callback function in which we describe what data we need from the result of our request:
const getOrganicResults = ({ organic_results }) => {
return organic_results.map((element) => {
const { link, title, condition = "No condition data", price = "No price data", shipping = "No shipping data", thumbnail = "No image" } = element;
return {
link,
title,
condition,
price: price && price.raw ? price.raw : `${price.from?.raw} - ${price.to?.raw}`,
shipping,
thumbnail,
};
});
};
| Code | Explanation |
|---|---|
organic_results |
an array that we destructured from response |
link, title, condition, price, shipping, thumbnail |
other data that we destructured from element of news_results array |
thumbnail = "No image" |
we set default value No image if thumbnail is undefined |
price: price && price.raw ? price.raw : '${price.from?.raw} - ${price.to?.raw}' |
in this line we use ternary operator to set vailid price. If we can get price and data with raw key we set it to our price, otherwise in price we set price.from and price.to |
Next, we wrap the search method from the SerpApi library in a promise to further work with the search results:
const getJson = (params) => {
return new Promise((resolve) => {
search.json(params, resolve);
})
}
getJson(params).then(getKnowledgeGraph).then(console.log)
And finally, we declare and run the function getResult that gets info from all pages between currentPage and pagesLimit and return it.
const getResults = async () => {
const organicResults = [];
while (true) {
if (currentPage > pagesLimit) break;
const json = await getJson(params);
if (json.search_information?.organic_results_state === "Fully empty") break;
organicResults.push(...(await getOrganicResults(json)));
currentPage++;
}
return organicResults;
};
getResults().then(console.log)
| Code | Explanation |
|---|---|
organicResults.push(...(await getOrganicResults(json))) |
in this code, we use spread syntax to split the array from result that was returned from getOrganicResults function into elements and add them in the end of organicResults array |
Full Code
const SerpApi = require("google-search-results-nodejs");
const search = new SerpApi.GoogleSearch(process.env.API_KEY); //your api key from serpapi.com
const searchString = "playstation"; // what we want to search
const pagesLimit = 10; // limit of pages for getting info
let currentPage = 1; // current page of the search
const params = {
engine: "ebay", // search engine
_nkw: searchString, // search query
ebay_domain: "ebay.com", // ebay domain of the search
_pgn: currentPage, // page of the search
};
const getOrganicResults = ({ organic_results }) => {
return organic_results.map((element) => {
const { link, title, condition = "No condition data", price = "No price data", shipping = "No shipping data", thumbnail = "No image" } = element;
return {
link,
title,
condition,
price: price && price.raw ? price.raw : `${price.from?.raw} - ${price.to?.raw}`,
shipping,
thumbnail,
};
});
};
const getJson = (params) => {
return new Promise((resolve) => {
search.json(params, resolve);
});
};
const getResults = async () => {
const organicResults = [];
while (true) {
if (currentPage > pagesLimit) break;
const json = await getJson(params);
if (json.search_information?.organic_results_state === "Fully empty") break;
organicResults.push(...(await getOrganicResults(json)));
currentPage++;
}
return organicResults;
};
getResults().then(console.log)Output
[
{
"link":"https://www.ebay.com/itm/324950767168?hash=item4ba8933640:g:yQsAAOSwU8phwB9l",
"title":"Sony PlayStation PS Vita OLED (PCH-1001) Firmware FW 3.60, 128GB - Ship in 1-DAY",
"condition":"Open Box",
"price":"$179.95",
"shipping":"Free shipping",
"thumbnail":"https://i.ebayimg.com/thumbs/images/g/yQsAAOSwU8phwB9l/s-l225.jpg"
},
{
"link":"https://www.ebay.com/itm/393419045168?hash=item5b999a3930:g:NzYAAOSwBPNiBoAk",
"title":"PS4 PlayStation 4 Sony Original Slim Pro 500GB 1TB 2TB Console Used Ship first",
"condition":"Pre-Owned",
"price":"$259.80 - $484.99",
"shipping":"Free shipping",
"thumbnail":"https://i.ebayimg.com/thumbs/images/g/NzYAAOSwBPNiBoAk/s-l225.jpg"
},
...and other results
]
Python Tutorial Integration
To get started with Python, install SerpApi's Python packages:
pip install google-search-resultsHere's a basic example of how to scrape eBay Search Results:
from serpapi import GoogleSearch
params = {
"api_key": "YOUR_SERPAPI_API_KEY",
"engine": "ebay",
"_nkw": "Coffee",
"ebay_domain": "ebay.com",
}
search = GoogleSearch(params)
results = search.get_dict()
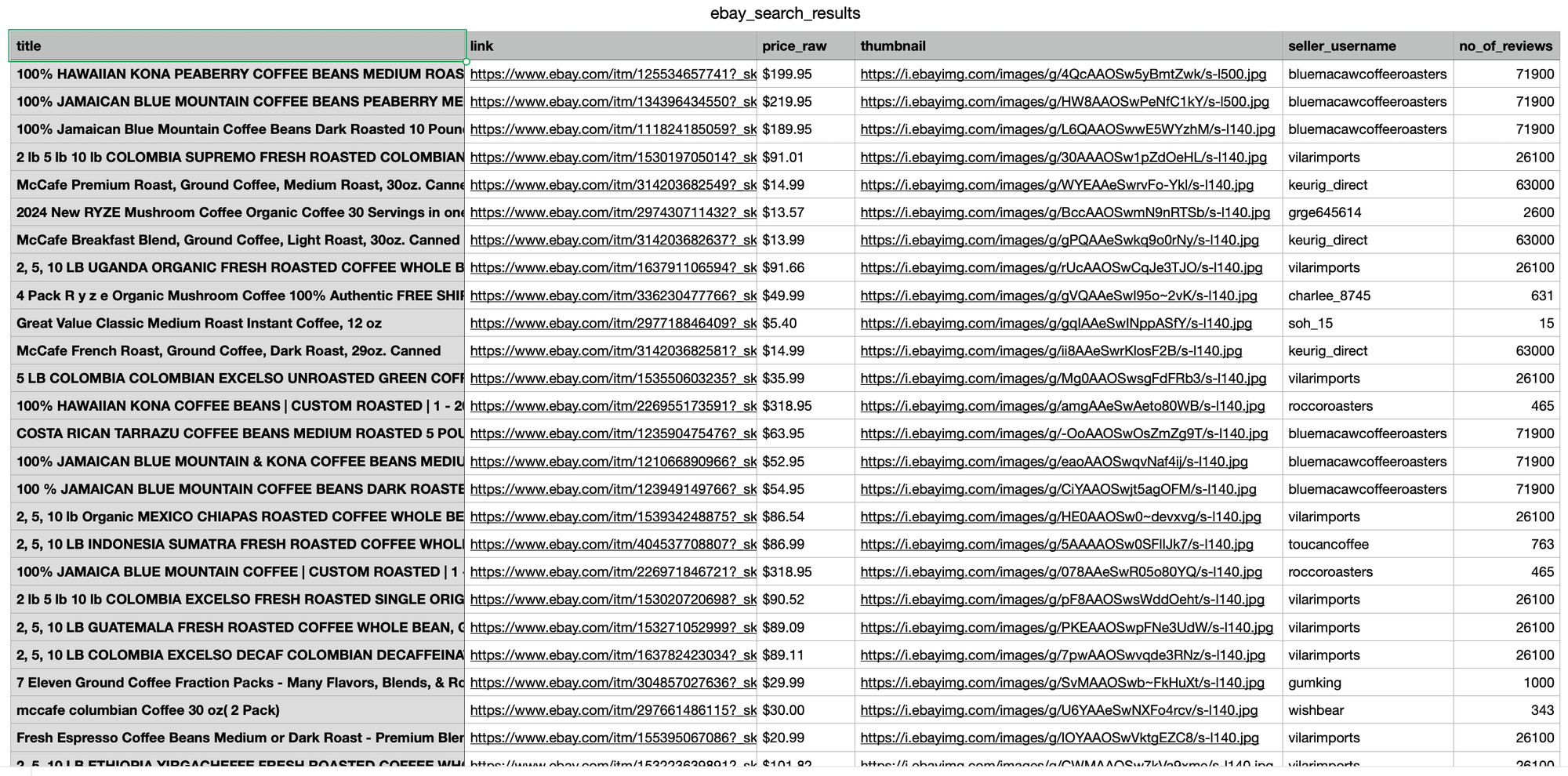
print(results)The code above returns the scraped data in JSON format. To analyze the results more easily, we can export the JSON fields to a CSV file using the following approach:
# ... continue from previous code
import csv
organic_results = results.get("organic_results", [])
header = ["title", "link", "price_raw", "thumbnail", "seller_username", "no_of_reviews"]
with open("ebay_search_results.csv", "w", encoding="UTF8", newline="") as f:
writer = csv.writer(f)
writer.writerow(header)
for organic_result in organic_results:
price = None
price_data = organic_result.get('price')
if price_data:
price = price_data.get('raw') if price_data.get('raw') else price_data.get('to', {}).get('raw')
writer.writerow([
organic_result.get('title'),
organic_result.get('link'),
price,
organic_result.get('thumbnail'),
organic_result.get('seller', {}).get('username'),
organic_result.get('seller', {}).get('reviews')
])Note that some products have price ranges, so we'll extract the highest price.
Ruby Tutorial Integration
Next, let's see how we can implement this in Ruby.
First, you need to install the SerpApi client in your Gemfile.
gem 'google_search_results'Then install the gem.
bundle installSet up the SerpApi credentials and search.
EbaySearch.api_key = "YOUR_API_KEY"
search = EbaySearch.new(_nkw: "coffee")
puts search.get_hashTo retrieve the eBay organic results for a given search query, you can use the following code:
results = search.get_hash[:organic_results]You can store eBay organic results in databases or export them to a CSV file.
require 'csv'
CSV.open("organic_results.csv", "w") do |csv|
csv << ["title", "link", "thumbnail", "price", "seller"]
results.each do |organic_result|
price = organic_result.dig(:price, :raw).presence || organic_result.dig(:price, :from, :raw)
csv << [organic_result[:title], organic_result[:link], organic_result[:thumbnail], price, organic_result.dig(:seller, :username)]
end
endParameters Explanation
Required parameters
_nkw: Defines the search query, similar to typing keywords directly into eBay’s search bar. This parameter becomes optional whencategory_idis provided.
Advanced parameters
ebay_domain: Specifies which regional eBay domain to scrape from.
(defaults:ebay.com).
Let's check on our playground by changing the domain to Germany.ebay_domain=ebay.de
https://serpapi.com/playground?engine=ebay&_nkw=Coffee&ebay_domain=ebay.de
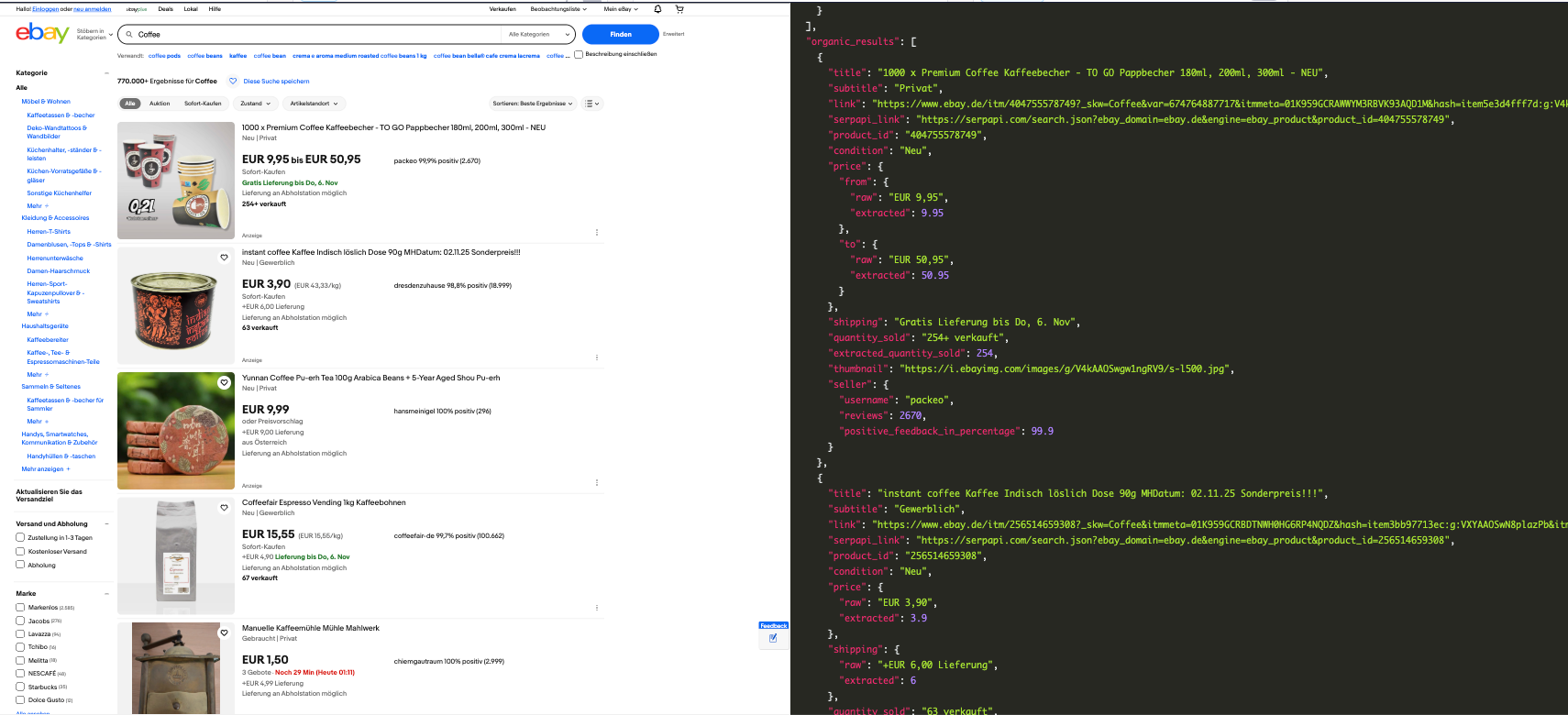
Notice from the result, the prices are in Euro and language is German.
Check the supported domains list for other domains.
_salic: Defines the country location for the search. Useful when you want results specific to a region._pgn: Defines the page number for pagination (default: 1)_ipg: Sets how many results to return per page. Available values are 25, 50 (default), 100, and 200._udlo: Defines the lowest price of items that should be included in the results._udhi: Defines the highest price of items that should be included in the results.
There are also many parameters supported to make your search more specific. Visit our eBay Search Engine Result API documentation for more information.
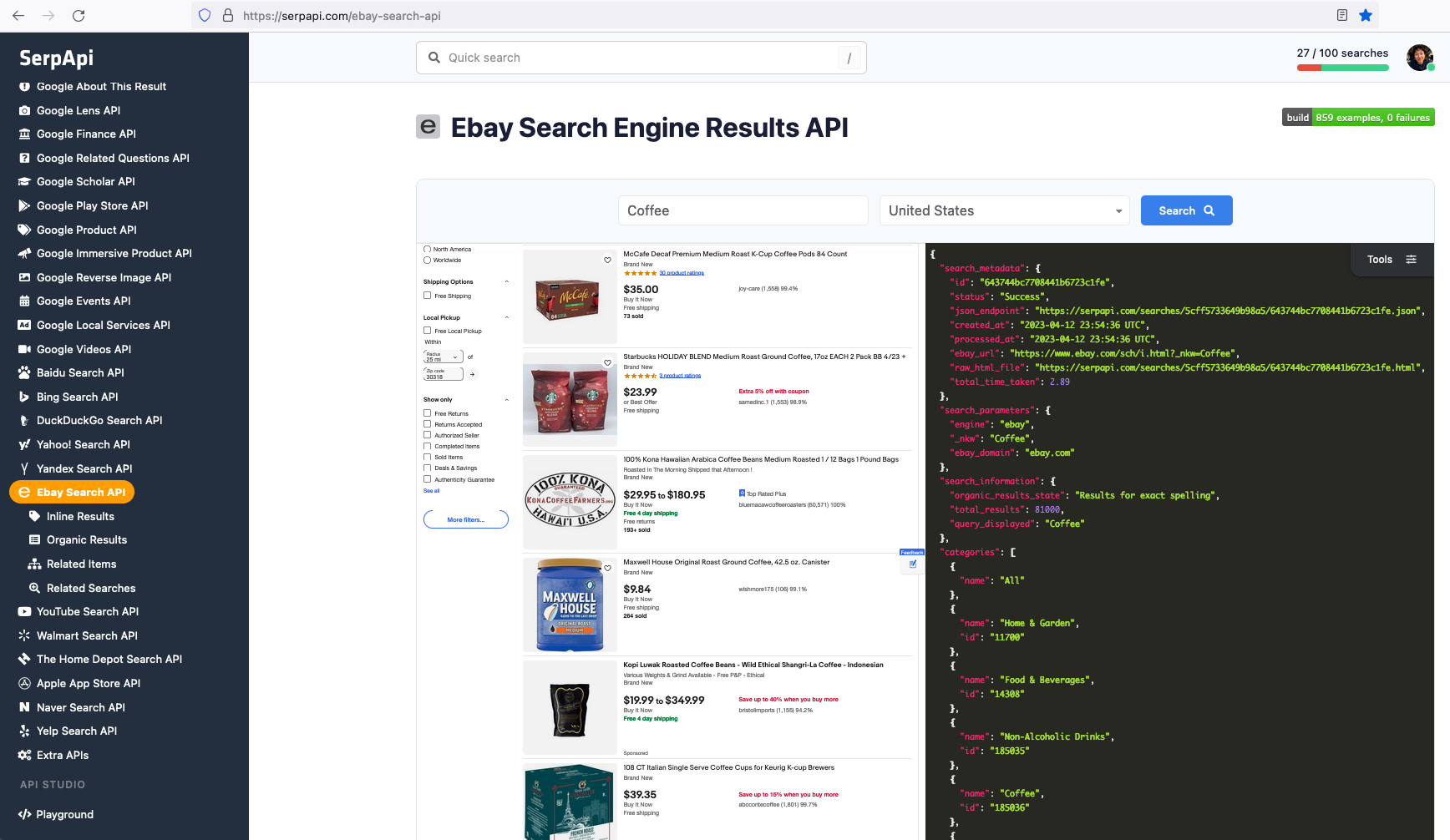
Beyond scraping eBay product listings and prices, many use cases require scraping eBay product reviews to gather customer sentiment insights.
How to Scrape eBay Product Reviews
This next section of the tutorial will show you how to easily scrape eBay product Reviews without dealing with dynamic HTML changes or anti-bot systems by using the eBay Product API.
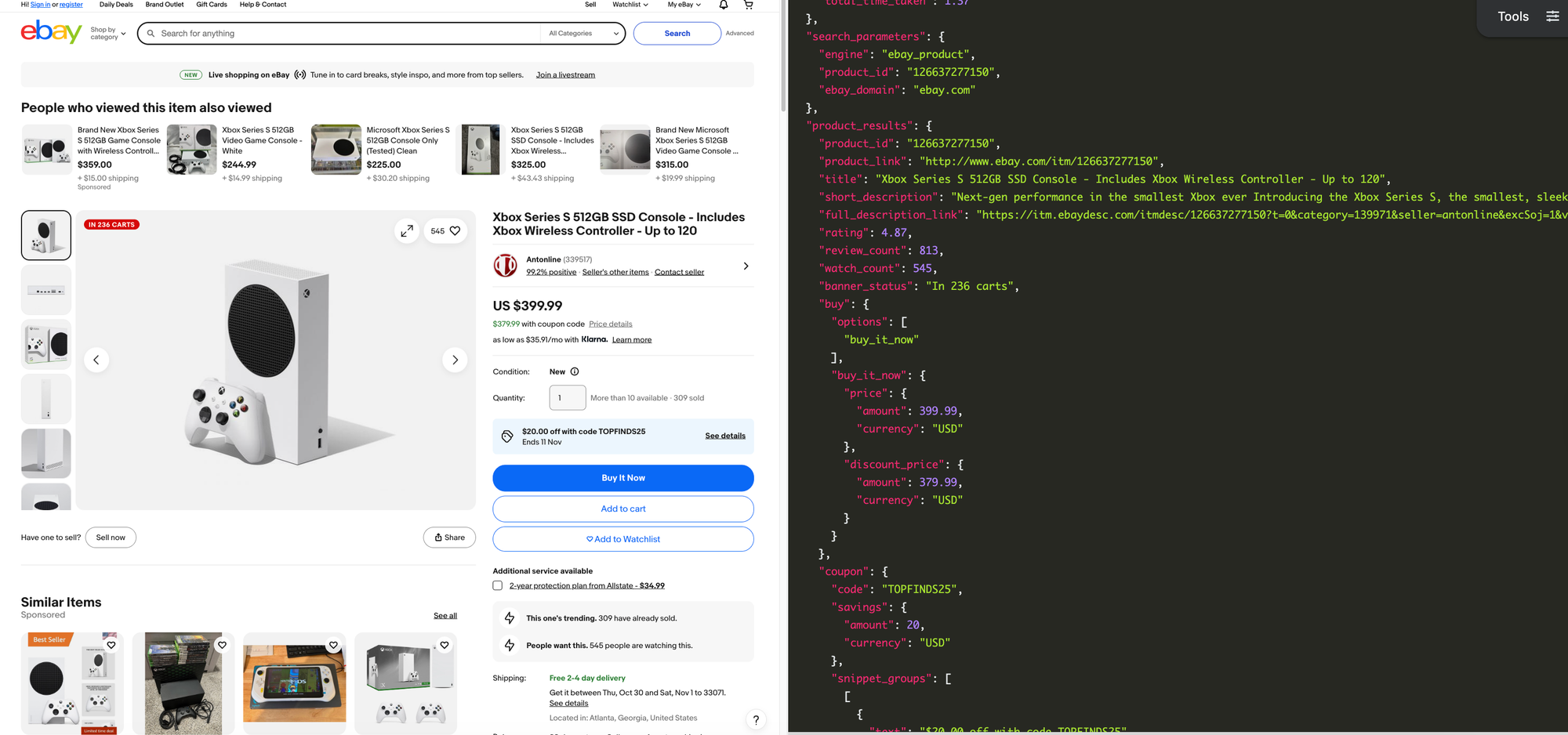
Each eBay product page contains detailed, valuable information. Beyond basic fields like product "titles" or "thumbnails", product pages include "short description", "customers' reviews", "shipping details", "coupon codes", "seller metadata", "related products", "details of product information", and more.
Python Tutorial Integration
At this point, I assume you already have your API key.
Here's a basic example of how to scrape an eBay product by ID (e.g., 126637277150)
from serpapi import GoogleSearch
params = {
"api_key": "YOUR_SERPAPI_API_KEY",
"engine": "ebay_product",
"product_id": "126637277150"
}
search = GoogleSearch(params)
results = search.get_dict()
print(results)Using JSON Restrictor to focus on Key Field
Since an eBay product page returns a large amount of structured data, you can use the JSON Restrictor to extract only specific fields.
In this example, our goal is to scrape eBay reviews without fetching unnecessary fields. Here’s how to return only the reviews section in the response:
# all previous code
params = {
"api_key": "YOUR_SERPAPI_API_KEY",
"engine": "ebay_product",
"product_id": "126637277150",
"json_restrictor": "seller_results.{reviews}"
}
# ...
# all previous codeSample JSON Output
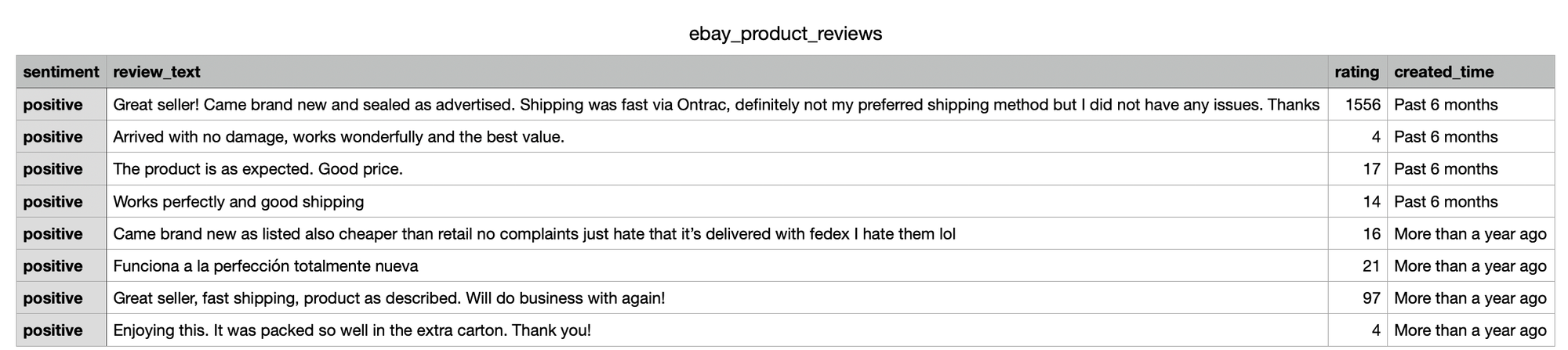
The response below shows the review data returned when scraping eBay product reviews using the json_restrictor :
{
"seller_results": {
"reviews": {
"groups": {
"this_product": {
"count": 30,
"list": [
{
"review_id": "2456079510019",
"sentiment": "positive",
"author": {
"username": "9***2",
"rating": 1556
},
"text": "Great seller! Came brand new and sealed as advertised. Shipping was fast via Ontrac, definitely not my preferred shipping method but I did not have any issues. Thanks",
"created_time": "Past 6 months",
"verified_purchase": true
},
.....
.....
.....
"see_all_link": "https://www.ebay.com/fdbk/mweb_profile?fdbkType=FeedbackReceivedAsSeller&item_id=126637277150&username=antonline&filter=feedback_page%3ARECEIVED_AS_SELLER&sort=RELEVANCEV2#tab1"
}
}
}
Next, we’ll parse the JSON fields and export the eBay product review data to CSV format:
# ... same as previous section
import csv
header = ["sentiment", "review_text", "rating", "created_time", ]
with open("ebay_product_reviews.csv", "w", encoding="UTF8", newline="") as f:
writer = csv.writer(f)
writer.writerow(header)
reviews = results.get("seller_results", {}).get("reviews", {}).get("groups", {}).get("this_product", {}).get("list", [])
for review in reviews:
writer.writerow([
review.get("sentiment"),
review.get("text"),
review.get('author', {}).get('rating'),
review.get("created_time")
])
Parameters Explanation
Required Parameter
product_id: The unique product identifier, which can be found in the product URL. For example:https://www.ebay.com/itm/{product_id}
Advanced Parameters
Apart from that, SerpApi supports other parameters as well to make your search results more specific:
ebay_domain: Defines the eBay domain to use (default:ebay.com)- See supported eBay domains.
locale: Defines the geographic location for the research.- See supported eBay locales.
lang: Defines the language of the results (default:en-US)- For example, if you set the
locale=jp, the result will be in Japanese, unless you overridelang=en-US
- For example, if you set the
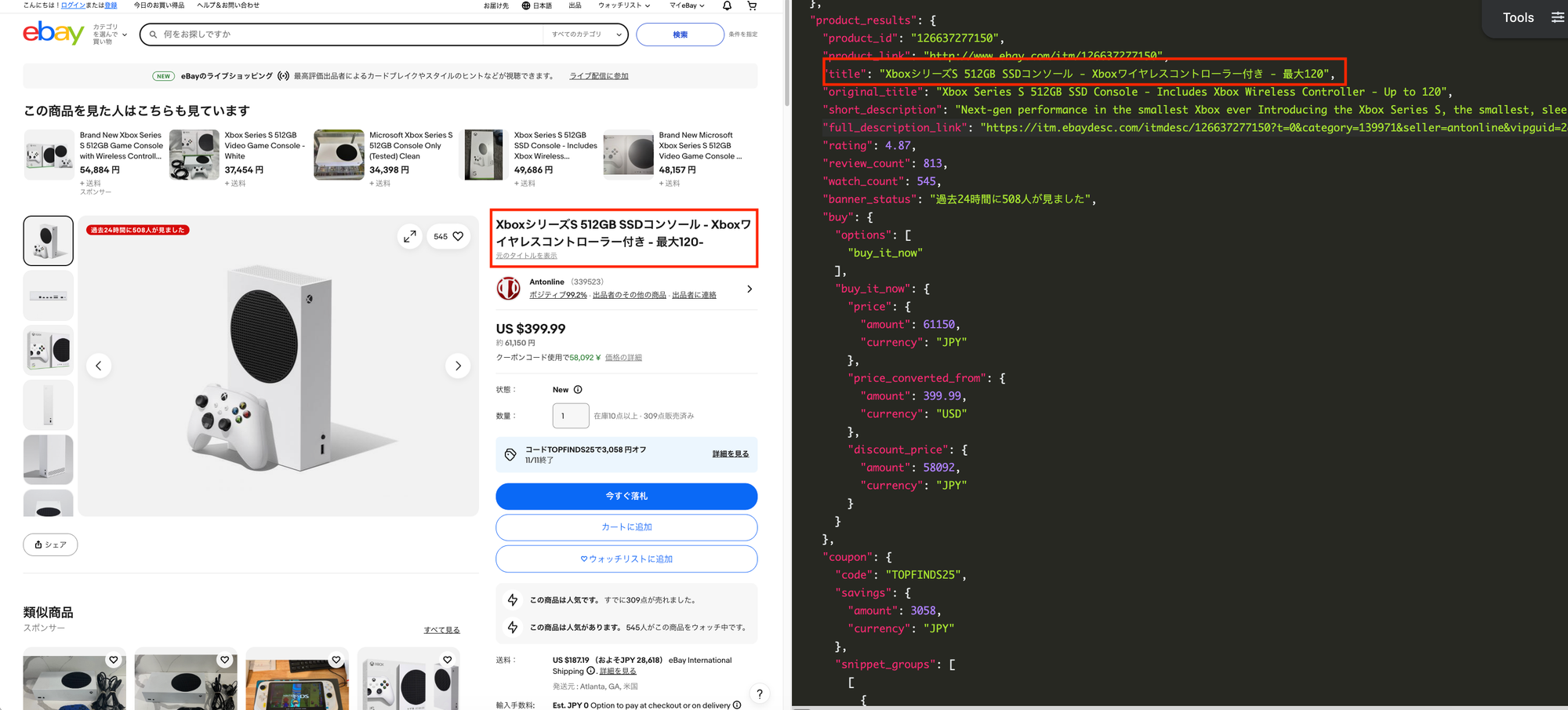
You can explore all parameters available on the product page in our eBay product API documentation.
Other programming languages
SerpApi provides official libraries for multiple programming languages including PHP, Go and also no-code platform such as n8n and direct integration in Google Sheets. Check out the full list in SerpApi Integrations for more details.
Conclusion
By combining the eBay Search API and Product API, you can scrape eBay product listings, extract eBay prices, and scrape eBay product reviews at scale without dealing with anti-bot challenges.
SerpApi returns clean JSON and provides official libraries for Python, JavaScript, Ruby, PHP, Go, and no-code platforms like n8n and Google Sheets.
Get started for free today and run up to 250 searches per month
If you have any questions, please feel free to contact us at contact@serpapi.com


