When people travel, one of the first things they do is compare hotels. Price alone isn’t enough - ratings, amenities, location, and recent reviews all factor into the decision. For developers building travel products, data analysts, or recommendation tools, this means turning rich but messy public data into structured, comparable insights.
Tripadvisor is one of the most valuable public sources for this kind of hotel intelligence, but extracting structured, comparable data at scale is difficult. In this post, we’ll walk through how to scrape hotel details from Tripadvisor using SerpApi’s Tripadvisor Place Results API with Python, and then compare hotels programmatically using the returned data.
What Are Tripadvisor Place Results?
The Tripadvisor Place Results page looks like this:
Here's an example URL: https://www.tripadvisor.com/1197076
A place on Tripadvisor represents a specific entity such as:
- A hotel
- A restaurant
- An attraction
For hotels, place results typically include:
- Hotel name and Tripadvisor URL
- Rating and reviews
- Pricing
- Address and geographic location
- Pictures and descriptions
- Nearby destinations
- Amenities and categories
This makes it a perfect input for hotel comparison workflows.
Get Hotel Results from Tripadvisor
Using SerpApi, you can request Tripadvisor place results by providing a hotel ID.
To get the hotel ID (place_id), you can make a request to our Tripadvisor Search API like this:
- Set
engineparameter totripadvisor - Provide a search query as the location (example: "Rome") and specify the
ssrc(Search Filter) parameter ash(for Hotels) - Specify your API key in the
api_keyparameter - Receive structured JSON with all hotels in that location
- Grab the
place_id
Here's an example in our Playground:

Then, for each hotel, we can get the Place Results using the place_id and sending the request to the Tripadvisor Place API.
The request for getting hotel details looks like:
- Set
engineparameter totripadvisor_place - Provide a
place_id(example:228406) - Specify your API key in the
api_keyparameter - Receive structured JSON with hotel details
Here's an example in our Playground:

The response gets us Tripadvisor place data for each hotel that would otherwise require manual parsing.
Some Basic Setup Steps
Setup your environment
Ensure you have the google-search-results library installed.
pip install google-search-resultsgoogle-search-results is our Python library. You can use this library to scrape search results from any of SerpApi's APIs.More About Our Python Libraries
We have two separate Python libraries serpapi and google-search-results, and both work perfectly fine. However, serpapi is a new one, and all the examples you can find on our website are from the old one google-search-results. If you'd like to use our Python library with all the examples from our website, you should install the google-search-results module instead of serpapi.
For this blog post, I am using google-search-results because all of our documentation references this one.
You may encounter issues if you have both libraries installed at the same time. If you have the old library installed and want to proceed with using our new library, please follow these steps:
- Uninstall
google-search-resultsmodule from your environment. - Make sure that neither
serpapinorgoogle-search-resultsare installed at that stage. - Install
serpapimodule, for example with the following command if you're usingpip:pip install serpapi
In addition to that, we'll need to install a few more libraries:
- Pandas: Useful for organizing data. Install this with:
pip install pandas - Matplotlib: Useful for building static plots. Install this with
pip install matplotlib
Get your SerpApi API key
To begin scraping data, first, create a free account on serpapi.com. You'll receive 250 free search credits each month to explore the API.
- Get your SerpApi API Key from this page.
- [Optional but Recommended] Set your API key in an environment variable, instead of directly pasting it in the code. Refer here to understand more about using environment variables. For this tutorial, I have saved the API key in an environment variable named "SERPAPI_API_KEY" in my .env file.
Import Libraries
Import all the necessary libraries for this project:
import csv
import os
from serpapi import GoogleSearch
from dotenv import load_dotenv
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
load_dotenv()Get Hotel Details using Python
For this tutorial, we'll look for 10 hotels in Rome. Once the setup is complete, here is a a simple Python script to get all hotels in Rome, and get hotels details for each one and add that to a list:
hotels = []
def get_hotel_results_from_tripadvisor(q):
params = {
"engine": "tripadvisor",
"q": q,
"api_key": os.environ["SERPAPI_API_KEY"],
}
results = GoogleSearch(params).get_dict()
return results.get("places", [])
def get_hotel_details_page_from_tripadvisor(place_id):
params = {
"engine": "tripadvisor_place",
"place_id": place_id,
"api_key": os.environ["SERPAPI_API_KEY"],
}
results = GoogleSearch(params).get_dict()
return results.get("place_result", {})
if __name__ == "__main__":
q = "Rome"
place_results = []
hotels = get_hotel_results_from_tripadvisor(q)
first_10_hotels = hotels[:10]
for result in first_10_hotels:
place_id = result.get("place_id", None)
if place_id:
hotel_details = get_hotel_details_page_from_tripadvisor(place_id)
place_results.append(hotel_details)Compare Hotels Programmatically
Let's first start by identifying fields that will be of importance to us.
Pick The Fields For Fair Comparison
To understand a place's identity:
place_result.nameplace_result.ratingplace_result.reviewsplace_result.hotel_starsplace_result.num_rooms
Useful for competitive context:
place_result.ranking→ parse numeric rankplace_result.reviews→ popularity signal
For understanding pricing:
price_range.lowprice_range.high- Lowest
offers[].extracted_price
Sub rating across various dimensions:
These are already numeric and normalized by Tripadvisor, making them perfect for comparison:
- Location
- Rooms
- Value
- Cleanliness
- Service
- Sleep Quality
Review highlights to extract insights from Reviews
reviews_highlights.categoryreviews_highlights.value
Define a Scoring Strategy
As a simple comparison strategy, we can compute three layers:
- Base Quality Score → from
subratings - Sentiments → from
reviews_highlights - Value-for-Money Score →
rating ÷ price
We can also weight the three differently when computing the final score for a hotel. For this tutorial, we'll use:
- 60% quality score (most reliable)
- 25% sentiment score (guest opinions)
- 15% price efficiency score
Let's define the plan for how we will use this scoring strategy on the list of place results we have already:
Get place_results for each hotel we want to compare
↓
Extract hotel features we want to compare for each hotel
↓
Compute scores for each hotel based on the scoring strategy above
↓
Store the hotel results in a table/dataframe
↓
Sort / filter / plot / export results
Code Solution
def extract_hotel_features(place_result):
HIGHLIGHT_SCORE_MAP = {
"Immaculate": 5.0,
"Abundant": 4.5,
"Convenient": 4.5,
"Good": 4.0,
"Inconsistent": 3.0,
"Average": 3.0,
"Dated": 2.0,
"Outdated": 2.0,
"Pricey": 2.0,
}
hotel = {
"name": place_result.get("name"),
"rating": place_result.get("rating"),
"review_count": place_result.get("reviews"),
"hotel_stars": place_result.get("hotel_stars"),
"num_rooms": place_result.get("num_rooms"),
}
# Ranking number
ranking = place_result.get("ranking")
if ranking:
hotel["city_rank"] = int(ranking.split("#")[1].split(" ")[0])
# Price range
price_range = place_result.get("price_range", {})
hotel["price_low"] = price_range.get("low")
hotel["price_high"] = price_range.get("high")
# Lowest observed price
offers = place_result.get("prices", {}).get("offers", [])
if offers:
hotel["lowest_price"] = min(
o["extracted_price"] for o in offers if "extracted_price" in o
)
# Subratings (primary scoring dimensions)
for item in place_result.get("subratings", []):
key = item["category"].lower().replace(" ", "_")
hotel[key] = item["score"]
# Review highlights (sentiment signals)
for h in place_result.get("reviews_highlights", []):
category = h["category"].lower()
value = h["value"]
hotel[f"{category}_sentiment"] = HIGHLIGHT_SCORE_MAP.get(value, 3.0)
return hotel
def compute_scores(hotel):
# 1. Base quality score (Tripadvisor subratings)
quality_fields = [
"location",
"rooms",
"value",
"cleanliness",
"service",
"sleep_quality",
]
quality_scores = [
hotel[f] for f in quality_fields if f in hotel
]
hotel["quality_score"] = round(
sum(quality_scores) / len(quality_scores), 2
)
# 2. Value-for-money score
if hotel.get("lowest_price") and hotel.get("rating"):
hotel["value_for_money"] = round(
hotel["rating"] / hotel["lowest_price"] * 100, 2
)
# 3. Sentiment score
sentiment_keys = [k for k in hotel if k.endswith("_sentiment")]
if sentiment_keys:
hotel["sentiment_score"] = round(
sum(hotel[k] for k in sentiment_keys) / len(sentiment_keys), 2
)
# 4. Final composite score
hotel["overall_score"] = round(
(
hotel["quality_score"] * 0.6 +
hotel.get("sentiment_score", 3) * 0.25 +
hotel.get("value_for_money", 0) * 0.15
),
2,
)
return hotelWith these basic functions in place, we can now compare hotels:
def compare_hotels(place_results):
hotels = []
for place_result in place_results:
hotel = extract_hotel_features(place_result)
hotel = compute_scores(hotel)
hotels.append(hotel)
hotels_sorted = sorted(
hotels,
key=lambda h: h.get("overall_score", 0),
reverse=True
)
df = pd.DataFrame(hotels_sorted)
# Select only the most useful comparison columns
comparison_df = df[
[
"name",
"overall_score",
"quality_score",
"sentiment_score",
"value_for_money",
"rating",
"review_count",
"city_rank",
"price_low",
"price_high",
"lowest_price",
]
]
return comparison_dfPlotting The Results
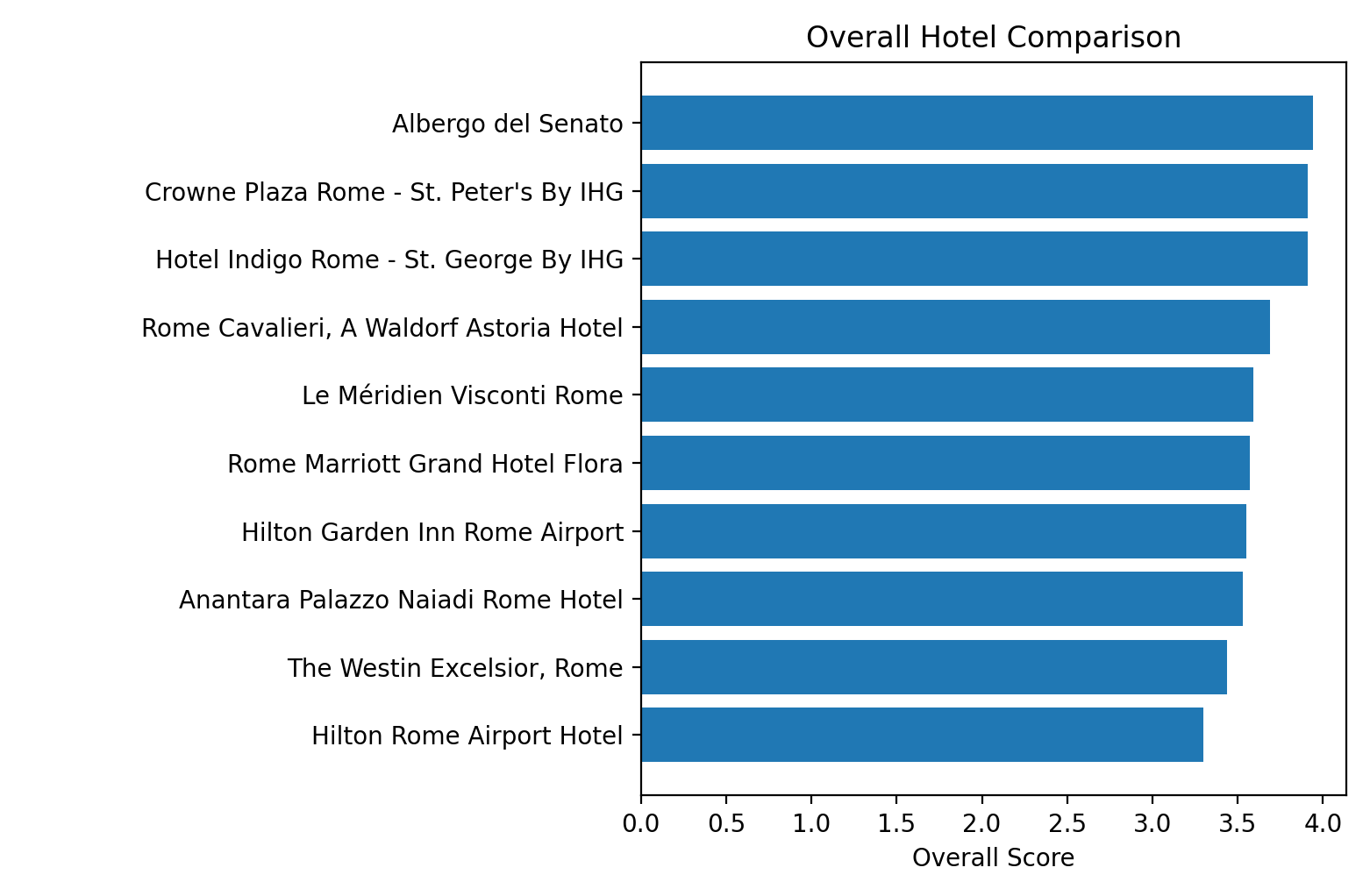
Best “at a glance” Ranking
Once we have the comparison_df, we can now plot the overall scores we computed earlier:
def plot_hotels_bar_chart(comparison_df):
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
df = comparison_df.sort_values("overall_score", ascending=False)
plt.figure()
plt.barh(df["name"], df["overall_score"])
plt.xlabel("Overall Score")
plt.title("Overall Hotel Comparison")
plt.gca().invert_yaxis()
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()What that looks like:
Price comparison (range chart)
Let's understand the price spread per hotel.
def plot_price_transparency(comparison_df):
plt.figure()
for i, row in enumerate(comparison_df.itertuples()):
plt.plot(
[row.price_low, row.price_high],
[i, i],
marker="o"
)
plt.yticks(range(len(comparison_df)), comparison_df["name"])
plt.xlabel("Price (€)")
plt.title("Hotel Price Ranges")
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()Calling this function plots a graph which makes pricing transparent:
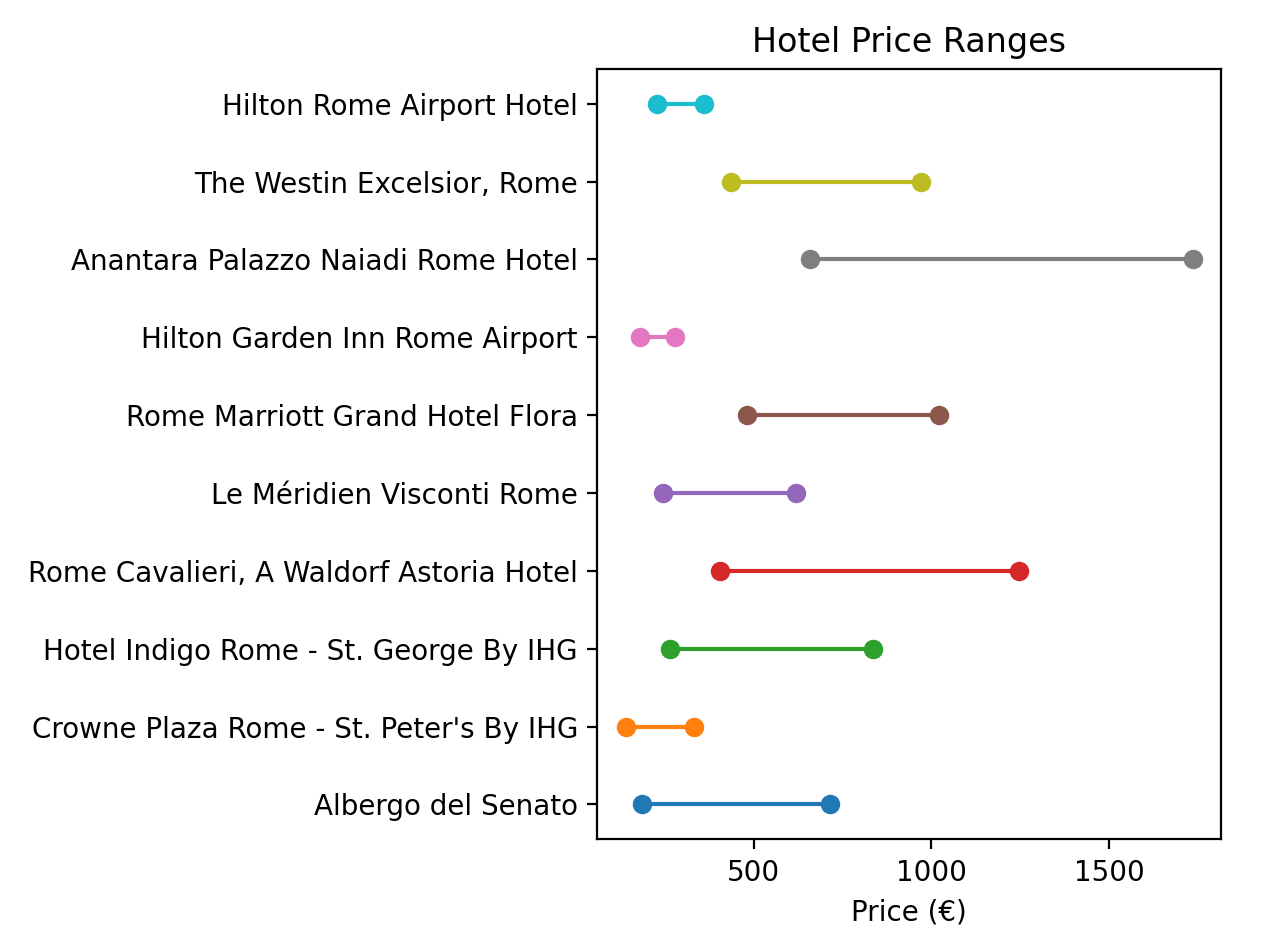
Practical Use Cases
This workflow is especially useful for:
- Travel startups building hotel comparison products
- Data teams analyzing hotel trends
- SEO teams creating location-based hotel content
- Investors and analysts tracking hotel performance across regions
Instead of manually browsing Tripadvisor for each hotel, you get structured, comparable insights at scale.
Conclusion
I hope that this tutorial helps you use SerpApi's Tripadvisor Place Results API and reliably extract hotel details and compare hotels in any destinations with minimal effort.
You can find all the code used in this blog post here:
https://github.com/sonika-serpapi/get-hotel-details-from-trip-advisor-and-compare-hotels
Feel free to reach out to us at contact@serpapi.com for any questions.
Relevant Links
Documentation
- Documentation for Tripadvisor Search API
- Documentation for Tripadvisor Place API
- Use Case Page: Build a Travel App Using SERP data
- Status page
- Plans and Pricing
Related Posts










